Best UPSC Academy in Hyderabad

- This event has passed.
16-April-2024-Special-Article
April 16, 2024 @ 7:00 am - 11:30 pm
STRICTER VIEW NEEDED IN CUSTODIAL DEATH CASES
Custodial death, the tragic demise of an individual under the watch of law enforcement or correctional facilities, remains a pressing issue in India. This phenomenon raises concerns about human rights violations, abuse of power, and the need for legal reforms to ensure justice and accountability.
About Custodial Death
- Definition: Death occurring when an individual is in the custody of law enforcement or correctional facilities.
- Causes: Excessive force, neglect, abuse, or incidental factors.
Types:
- Police Custody: Due to excessive force, torture, or denial of medical care.
- Judicial Custody: Overcrowding, poor hygiene, lack of medical facilities, or inmate violence.
- Army/Paramilitary Custody: Torture or extrajudicial killings.
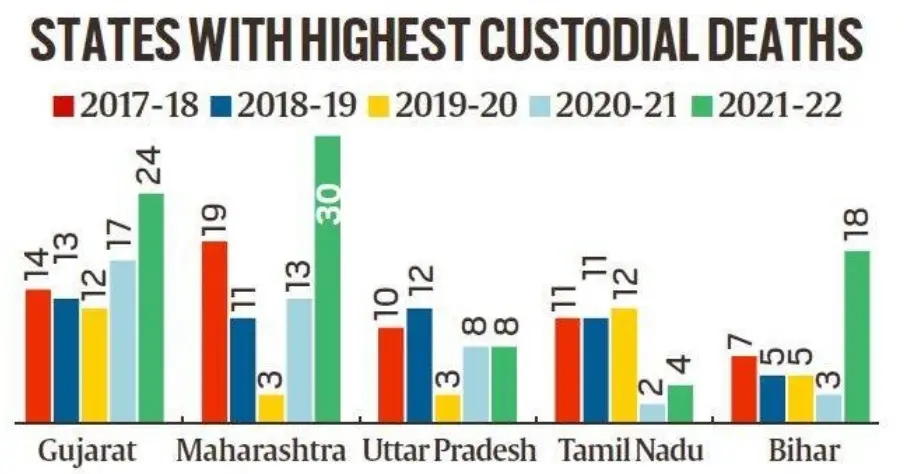
Why is Restricting Custodial Deaths Necessary?
- Human Rights Violation: Contradicts the right to fair treatment and protection from torture.
- International Obligations: India’s commitment to the United Nations Convention Against Torture (UNCAT).
- Extradition Challenges: Hinders extradition proceedings for economic offenders, e.g., Vijay Mallya.
- Mental Health Impact: Traumatic experiences can lead to severe psychological distress.
Constitutional and Legal Safeguards
Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 21: Right to life and personal liberty, includes protection from torture.
- Article 20: Protection against arbitrary punishment, double jeopardy, and self-incrimination.
- Selvi v. State of Karnataka: Consent required for narco-analysis, polygraph, and brain-mapping tests.
Legal Protections:
- Section 24, Indian Evidence Act: Confessions under threat are inadmissible.
- Sections 330 and 331, IPC: Criminalize causing hurt or grievous hurt for extracting confession.
- Section 41, CrPC: Safeguards for transparent arrests, protection, and legal representation.
International Conventions Against Custodial Torture
- International Human Rights Law, 1948: Protection against torture and enforced disappearances.
- United Nations Charter, 1945: Dignified treatment of prisoners, respecting fundamental freedoms.
- Nelson Mandela Rules, 2015: Prohibition of torture and ill-treatment.
- UNCAT: Global treaty to prevent torture and inhuman treatment.
Measures to Combat Custodial Torture
Strengthening Legal Systems:
- Enact Comprehensive Legislation: Criminalize custodial torture as directed in Prakash Singh Case 2006.
- Separate Investigation and Law and Order: Improve policing, establish State Security Commissions (SSC), and a National Security Commission.
Police Reforms and Sensitization:
- Enhanced Training: Emphasize human rights, professionalism, and empathy.
- Culture of Accountability: Promote transparency and accountability in law enforcement.
- Oversight Mechanisms: Monitor and address custodial torture cases effectively.
Empowering Civil Society and Human Rights Organizations:
- Active Advocacy: Civil society organizations should advocate for victims of custodial torture.
- NHRC Expansion: Extend jurisdiction to cases of human rights violations by armed forces and allow inquiries even after a year.
- Legal Assistance: Provide support and legal aid to victims and families.
Collaboration with International Bodies:
- Seek Redress and Justice: Collaborate with global human rights bodies and organizations to address custodial torture cases effectively.
Mains Question:
- Discuss the significance of strengthening legal frameworks and implementing police reforms to address custodial deaths in India. (150 WORDS)

