WORLD HISTORY
The Fall of Constantinople: Prelude to a New Era
In the annals of world history, few events are as momentous and transformative as the Fall of Constantinople. This singular event, which transpired on May 29, 1453, marked not only the end of the Byzantine Empire but also heralded a seismic shift in the geopolitical landscape of Europe and Asia.

The fall of this ancient city, long considered the bastion of Eastern Christianity and the gateway between Europe and the Middle East, was both a culmination and a catalyst—signaling the end of medieval Christendom and the dawn of a new epoch in global history.
Constantinople, established by Emperor Constantine the Great in 330 AD, had been the jewel of the Byzantine Empire. Strategically positioned on the crossroads of Europe and Asia, it was a hub of commerce, culture, and religion.
Its impregnable walls and prosperous economy made it the envy of the known world. For over a millennium, it withstood numerous sieges, invasions, and challenges, maintaining its status as a vital center of trade and a bastion of Christian orthodoxy.
Yet, by the mid-15th century, the Byzantine Empire had been reduced to a mere shadow of its former self. The once-great empire had been eroded by centuries of warfare, internal strife, and the relentless expansion of neighboring powers.
The rise of the Ottoman Turks, led by Sultan Mehmed II, presented an existential threat to the city. The Ottomans, whose ambitions extended across Europe and the Middle East, saw the capture of Constantinople as essential to their quest for dominance.
The fall of Constantinople was not an isolated event but the culmination of a prolonged siege that lasted from April 6 to May 29, 1453. The Ottoman forces, vastly outnumbering the defenders, employed cutting-edge military technology, including massive cannons and sophisticated siege tactics. The defenders, led by Emperor Constantine XI Palaiologos, fought valiantly but were ultimately overwhelmed by the sheer scale and intensity of the Ottoman assault.
The city’s fall had profound implications far beyond the immediate loss of territory. It marked the end of Christian Byzantine rule in the eastern Mediterranean and the consolidation of Ottoman power, which would profoundly influence the course of history in both Europe and Asia. The Ottoman Empire, now firmly established with Constantinople as its capital, expanded rapidly, reshaping the political and cultural landscape of the region.
Moreover, the fall of Constantinople accelerated the decline of the medieval period and the emergence of the Renaissance. The disruption of traditional trade routes through the city prompted European powers to seek new paths to the East, igniting the Age of Exploration and the eventual discovery of the Americas. The intellectual and cultural exchanges that followed contributed to the flourishing of new ideas and advancements that defined the Renaissance and set the stage for the modern world.
Thus, the Fall of Constantinople stands as a watershed moment in history, embodying both the end of an era and the beginning of another. It represents the intersection of decline and transformation, a poignant reminder of how singular events can alter the course of civilizations and shape the future of the world. As we delve into the complexities of this historical watershed, we are not only exploring the decline of an empire but also witnessing the birth of a new world order.
The Renaissance in Europe: A Flourishing of Art, Science, and Thought (14th to 17th Century)
The Renaissance, spanning roughly from the 14th to the 17th century, represents one of the most transformative periods in European history. This era marked a profound revival of classical learning and wisdom, leading to significant advancements in art, science, politics, and philosophy. The Renaissance, meaning “rebirth,” emerged from the ashes of the Middle Ages, fostering an intellectual and cultural revolution that shaped the modern world.
Origins and Early Developments (14th Century)
The Renaissance began in Italy, a region rich in the remnants of Roman antiquity and a hub of trade and commerce. Florence, under the patronage of the Medici family, was the epicenter of early Renaissance art and culture. Influential figures such as Dante Alighieri and Petrarch laid the intellectual groundwork with their works in literature and philosophy, which emphasized humanism—the study of classical texts and a focus on human potential and achievements.
During this period, Giotto di Bondone revolutionized art with his frescoes, moving away from the Byzantine style of flat, symbolic representation to a more naturalistic portrayal of the human form and space. His work, notably in the Arena Chapel in Padua, demonstrated a new emphasis on realism and emotional expression.
The Height of Artistic Achievement (15th Century)
The 15th century witnessed an explosion of artistic and scientific innovation. Artists such as Sandro Botticelli, Leonardo da Vinci, and Michelangelo contributed to a burgeoning culture of creativity.
Botticelli’s “The Birth of Venus” and “Primavera” showcased his mastery of mythological themes and delicate beauty. Leonardo da Vinci, a true polymath, made groundbreaking contributions across various fields, including anatomy, engineering, and painting. His masterpieces “The Last Supper” and “Mona Lisa” exemplify the Renaissance ideals of perspective, proportion, and human emotion.
Michelangelo Buonarroti, another towering figure, left an indelible mark with his sculptural works such as “David” and “Pieta,” and his extraordinary frescoes on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel in Vatican City. His work in architecture, including the design of St. Peter’s Basilica, further cemented his legacy.
Scientific Revolution and Humanism (16th Century)
The 16th century expanded the Renaissance’s reach into the sciences and philosophy. The scientific revolution, ignited by figures such as Nicolaus Copernicus and Galileo Galilei, challenged medieval views of the cosmos.
Copernicus’ heliocentric theory, proposed in his work “De revolutionibus orbium coelestium” (1543), argued that the Earth revolved around the Sun, contradicting the long-held geocentric model. Galileo’s telescopic observations and support of Copernican theory brought him into conflict with the Catholic Church but marked a significant advancement in scientific understanding.
Humanism, a cornerstone of the Renaissance, continued to thrive through scholars like Erasmus of Rotterdam and Thomas More. Erasmus’ “In Praise of Folly” (1511) critiqued the corruption of the Church and advocated for reform, while More’s “Utopia” (1516) presented an idealized society, reflecting Renaissance humanist ideals of social and political philosophy.
The Renaissance Beyond Italy (16th to 17th Century)
While Italy was the cradle of Renaissance art and thought, the movement gradually spread across Europe. In France, the Renaissance took root under the patronage of King Francis I, leading to the flourishing of French Renaissance art and architecture. The Château de Chambord, with its distinctive architecture and innovative design, exemplifies this period of French cultural development.
In England, the Renaissance manifested in literature with the works of William Shakespeare, whose plays and sonnets captured the complexity of human experience and explored themes of power, love, and betrayal. The Elizabethan era saw a flowering of drama, poetry, and exploration, marking a vibrant period of cultural and intellectual activity.
The Northern Renaissance, encompassing the Low Countries, Germany, and England, was characterized by a focus on detailed realism and the integration of Renaissance humanism with local traditions. Artists such as Albrecht Dürer and Jan van Eyck pioneered techniques in oil painting and woodcuts, influencing the broader European artistic landscape. Dürer’s engravings and woodcuts, including “Melencolia I” and “Knight, Death, and the Devil,” reflect a synthesis of Renaissance ideals and Northern European detail.
Legacy and Conclusion
The Renaissance era profoundly shaped the course of Western history. Its emphasis on human potential, classical learning, and artistic innovation paved the way for the modern world. The period fostered advances in science, art, and literature that continue to influence contemporary culture and thought.
As Europe transitioned into the Baroque era, the Renaissance’s legacy endured, laying the intellectual and cultural foundations for subsequent developments in art, science, and philosophy. The Renaissance was not merely a historical moment but a dynamic and ongoing influence that continues to inspire and inform the modern world.
EFFECTS OF THE RENAISSANCE
The Renaissance, spanning from the 14th to the 17th century, had profound and far-reaching effects on European society, economy, and culture. This transformative period not only reshaped the landscape of art and science but also had significant implications for social structures and economic practices. Here’s an overview of how the Renaissance impacted these aspects:
Society
Humanism and Education:
- Humanist Philosophy: The Renaissance fostered a renewed interest in classical texts and ideas, which led to the development of humanism. This intellectual movement emphasized the study of humanities—grammar, rhetoric, history, and moral philosophy—based on classical antiquity. This shift encouraged individuals to focus on human potential and achievements, fostering a more secular outlook.
- Educational Reform: Education became more accessible, with the establishment of new schools and universities across Europe. The curriculum expanded beyond theology to include subjects such as literature, history, and the arts. This broadening of educational scope contributed to a more educated and literate populace.
Social Mobility and Individualism:
- Rise of the Middle Class: Economic growth during the Renaissance led to the emergence of a more affluent and influential middle class. This new social stratum gained prominence and began to challenge the traditional dominance of the nobility and clergy.
- Individualism: The Renaissance emphasized individual achievement and personal expression. Artists, writers, and thinkers were celebrated for their personal contributions, which led to a shift from collective to individual recognition in society.
Political and Social Structures:
- Political Changes: The Renaissance period saw the decline of feudalism and the rise of more centralized nation-states. Monarchs and central authorities began to consolidate power, leading to more structured and bureaucratic forms of governance.
- Social Reform: There was an increased focus on civic life and the responsibilities of individuals within society. The Renaissance promoted ideas about the role of citizens and governance, influencing future political thought and structures.
Economy
Commercial Expansion:
- Trade and Exploration: The Renaissance era was marked by a surge in exploration and trade. Advances in navigation and cartography facilitated overseas exploration, leading to the establishment of new trade routes and colonial empires. This expansion contributed to economic growth and the exchange of goods, cultures, and ideas.
- Banking and Finance: The period saw the development of modern banking practices. Prominent banking families like the Medici in Florence played a significant role in financing trade, art, and political ventures. The growth of banking and financial institutions helped stimulate economic activity and investment.
Economic Theories and Practices:
- Mercantilism: The Renaissance period laid the groundwork for mercantilism, an economic theory that emphasized the accumulation of wealth through trade and the establishment of colonies. Mercantilism influenced European economic policies and practices for centuries.
- Craftsmanship and Industry: There was a rise in craftsmanship and the production of luxury goods, such as textiles and art. The increased demand for these products contributed to the growth of various industries and the commercialization of art.
Culture
Art and Architecture:
- Artistic Innovation: The Renaissance ushered in a new era of artistic achievement, characterized by advances in techniques such as perspective, chiaroscuro (the use of light and shadow), and realistic portrayal of human figures. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael produced works that remain celebrated for their beauty and innovation.
- Architectural Advancements: Renaissance architecture saw a revival of classical forms and the development of new architectural styles. The use of domes, columns, and pilasters became prominent, as seen in masterpieces like St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome and the Florence Cathedral.
Literature and Philosophy:
- Literary Flourishing: The Renaissance was a golden age for literature. Writers such as Dante Alighieri, Geoffrey Chaucer, and later, William Shakespeare, explored themes of human experience, politics, and morality. Their works continue to influence literature and thought.
- Philosophical Inquiry: Renaissance thinkers, including Niccolò Machiavelli and Erasmus, explored new ideas about politics, ethics, and human nature. Their writings contributed to the development of modern political and ethical theories.
Scientific Advancements:
- Scientific Revolution: The Renaissance laid the groundwork for the Scientific Revolution. Innovations in scientific thought and methodology, driven by figures such as Galileo Galilei and Nicolaus Copernicus, led to groundbreaking discoveries and a shift in understanding the natural world.
Cultural Exchange:
- Cultural Renaissance: The period facilitated the exchange of cultural and intellectual ideas across Europe. The spread of Renaissance art, literature, and scientific knowledge had a unifying effect on European culture, fostering a shared intellectual and artistic heritage.
The Renaissance was a period of significant transformation that influenced various facets of European life. It reshaped societal structures, catalyzed economic development, and fostered a rich cultural and intellectual environment. The effects of the Renaissance extended well beyond its time, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to resonate in the modern world.
The Conditions Leading to the Industrial Revolution in Europe (1760–1840)
The Industrial Revolution, a transformative period from the late 18th to the early 19th century, marked the transition from agrarian economies to industrialized and urbanized societies. The revolution began in Britain and gradually spread across Europe, fundamentally altering economies, societies, and technologies. Several crucial conditions paved the way for this profound shift, shaping the trajectory of modern industrial society.
1. Economic Factors
Agricultural Revolution:
- Innovations in Farming: The Agricultural Revolution, preceding the Industrial Revolution, introduced new farming techniques and tools. Innovations such as the seed drill, selective breeding of livestock, and crop rotation increased agricultural productivity and efficiency.
- Increased Food Production: Enhanced agricultural practices led to surplus food production, supporting a growing population. This surplus created a labor force that could transition from agriculture to industrial work, fueling urbanization and industrial labor markets.
Capital Accumulation:
- Trade and Colonization: The expansion of trade and colonization provided European nations with vast resources and capital. Profits from colonial ventures and international trade were reinvested into industrial ventures, providing the necessary financial backing for industrial enterprises.
- Banking and Investment: The development of banking systems and financial institutions facilitated the accumulation and investment of capital. Investors and entrepreneurs had access to funds needed for industrial ventures, technological innovation, and infrastructure development.
Markets and Demand:
- Population Growth: The population increase created a larger domestic market for industrial goods. The growing demand for consumer products and goods spurred industrial production and innovation.
- Consumer Culture: The rise of a consumer culture, driven by increased disposable income and urbanization, further stimulated demand for manufactured goods, encouraging industrial expansion.
2. Technological Innovations
Mechanization:
- Textile Industry: The textile industry was among the first to undergo mechanization. Key inventions such as James Hargreaves’s spinning jenny, Richard Arkwright’s water frame, and Samuel Crompton’s spinning mule revolutionized textile production, increasing efficiency and output.
- Steam Power: The development and widespread use of the steam engine, notably improved by James Watt, transformed industrial production. Steam power enabled the operation of machinery and transportation, reducing reliance on manual labor and increasing production capabilities.
Transportation:
- Railways: The expansion of railways, beginning with George Stephenson’s locomotive in the early 19th century, revolutionized transportation. Railways facilitated the movement of goods and raw materials, linking industrial centers with markets and reducing transportation costs.
- Canals and Roads: Prior to the railway boom, the construction of canals and improved road networks played a crucial role in transporting raw materials and finished products, enhancing regional and national trade.
Iron and Steel Production:
- Bessemer Process: The invention of the Bessemer process for producing steel from iron in the 1850s (slightly after the primary period but influenced by earlier innovations) significantly lowered the cost of steel production. This development paved the way for advancements in construction, machinery, and infrastructure.
3. Social and Political Factors
Political Stability:
- British Stability: Britain’s relative political stability and effective governance provided a conducive environment for industrial growth. The absence of major internal conflicts and the support of policies favoring economic development contributed to the country’s industrial success.
- Legal and Property Rights: Strong property rights and a legal framework supporting private enterprise encouraged investment and entrepreneurship. The protection of intellectual property and patents promoted innovation and technological progress.
Social Changes:
- Urbanization: The migration of people from rural areas to cities, driven by agricultural surplus and industrial job opportunities, accelerated urbanization. Urban centers became hubs of industrial activity and innovation, fostering a culture of industrialization.
- Labor Market: The growth of industries created a labor market that demanded a large workforce. This shift from agrarian work to factory labor was facilitated by changes in labor laws, such as the Factory Acts, which gradually improved working conditions and regulated child labor.
4. Scientific and Intellectual Movements
Enlightenment Ideas:
- Scientific Inquiry: The Enlightenment, with its emphasis on reason and empirical evidence, laid the groundwork for scientific advancements. The spirit of inquiry and experimentation influenced technological innovation and industrial practices.
- Economic Theories: The development of economic theories by thinkers such as Adam Smith, who advocated for free markets and economic liberalism, influenced industrial policies and practices, promoting the expansion of industry and commerce.
Education and Knowledge:
- Technical Education: The establishment of technical schools and institutions provided specialized education in engineering, mechanics, and industrial processes. This educated workforce was crucial for implementing and advancing industrial technologies.
- Public Libraries and Scientific Societies: The growth of public libraries and scientific societies facilitated the dissemination of knowledge and innovation, supporting the industrial and technological progress of the era.
5. International Factors
Global Trade Networks:
- Colonial Resources: The exploitation of colonial resources, including raw materials such as cotton, coal, and minerals, provided the raw materials needed for industrial production. Colonial trade routes and networks facilitated the global distribution of manufactured goods.
- Competitive Pressures: European nations competed for dominance in global trade and industrial production. This competition drove technological advancements and industrial expansion as countries sought to outperform their rivals.
Industrial Espionage and Knowledge Transfer:
- Knowledge Transfer: The spread of industrial knowledge from Britain to other European countries and the United States, through espionage and migration of skilled workers, facilitated the rapid adoption of industrial practices and technologies.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution not only reshaped Europe but also had profound global implications, setting the stage for the modern industrial world. The legacy of this period continues to influence contemporary society, economy, and technology.
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Society and Economy
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century and continued into the 19th century, brought about profound changes in both the societal and economic structures of industrializing nations. This period marked a significant shift from agrarian economies based primarily on manual labor to industrialized economies characterized by mechanized production and technological innovation. The effects of this transformative era were far-reaching and multifaceted, influencing various aspects of life.
Economic Impact
Transformation of Production Methods:
- Mechanization: The introduction of machinery, such as the spinning jenny and the steam engine, revolutionized production processes. Factories emerged, leading to mass production of goods, which increased efficiency and output while reducing labor costs.
- Industrial Growth: The rise of industries, particularly in textiles, iron, and coal mining, contributed to economic growth. This expansion created new job opportunities and stimulated investment in infrastructure and technology.
Urbanization and Demographic Changes:
- Population Migration: The promise of jobs in industrial cities led to significant rural-to-urban migration. Cities expanded rapidly, leading to the growth of urban centers and the rise of new social and economic dynamics.
- Changing Workforce: The labor market shifted from agriculture to factory work. This transition often involved long working hours and challenging conditions, but it also offered better wages compared to agricultural labor.
Economic Inequality:
- Wealth Concentration: The Industrial Revolution led to significant wealth accumulation for industrialists and entrepreneurs, contributing to economic disparities. While some benefited from industrialization, many workers faced poor living conditions and low wages.
- Class Distinctions: The period saw the emergence of a distinct industrial capitalist class and a working class. Social stratification became more pronounced, with stark differences between the wealthy industrialists and the working poor.
Development of Capitalism:
- Expansion of Markets: The increase in production capacity allowed for the expansion of domestic and international markets. This growth spurred the development of global trade networks and capitalism.
- Financial Institutions: The Industrial Revolution saw the rise of modern financial institutions, including banks and stock exchanges, which facilitated investment and economic expansion.
Technological Advancements:
- Infrastructure: Advances in transportation, such as railways and steamships, improved the efficiency of moving goods and people. This development played a crucial role in supporting industrial growth and market expansion.
- Innovation: The era was marked by significant technological innovations that laid the groundwork for future advancements. Inventions such as the telegraph and telephone revolutionized communication and business operations.
Social Impact
Living Conditions:
- Urban Housing: Rapid urbanization led to overcrowded and unsanitary living conditions in many industrial cities. The lack of proper housing and infrastructure contributed to health problems and poor quality of life for many workers.
- Public Health: Industrialization brought about public health challenges, including the spread of diseases due to inadequate sanitation and poor living conditions in urban areas.
Labor Conditions:
- Workplace Environment: Factory work often involved long hours, low wages, and dangerous conditions. Child labor was prevalent, and workers faced health hazards from exposure to harmful substances and unsafe machinery.
- Labor Movements: The difficult working conditions led to the rise of labor movements and the push for reforms. Workers organized strikes and unions to advocate for better wages, working hours, and improved conditions.
Social Mobility:
- Opportunities for Advancement: Industrialization created new opportunities for social mobility. Individuals who acquired skills and education could improve their socio-economic status and enter new professions.
- Educational Access: The need for skilled workers led to an increase in educational opportunities. Technical schools and vocational training programs emerged to meet the demands of the growing industrial economy.
Family Dynamics:
- Changing Roles: The shift to factory work altered traditional family roles. Many families experienced changes in dynamics as women and children entered the workforce, and family structures adapted to new economic realities.
- Child Labor: While industrialization provided economic opportunities, it also led to the exploitation of child labor. Reformers and social activists campaigned for legislation to protect children and regulate labor practices.
Cultural and Social Changes:
- Rise of the Middle Class: The growth of industry contributed to the expansion of the middle class, including industrialists, managers, and professionals. This class became a significant social and economic force.
- Cultural Shifts: Industrialization influenced cultural and social norms. New values related to work, progress, and consumerism emerged, shaping modern attitudes and behaviors.
Global Impact:
- Colonial Expansion: The demand for raw materials and markets for manufactured goods spurred colonial expansion. European powers increased their control over territories in Africa, Asia, and the Americas, leading to global economic and social changes.
- International Trade: The expansion of industrial production facilitated international trade, leading to increased economic interdependence among nations and the development of a global economy.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution while it spurred economic growth and technological advancement, it also highlighted social inequalities and the need for reform. The legacy of the Industrial Revolution continues to influence modern economic systems, labour practices, and social structures, making it one of the most pivotal periods in human history.
The Industrial Revolution in the United States and Its Impact on Society and Economy
The Industrial Revolution in the United States, spanning from the early 19th century to the early 20th century, marked a period of significant transformation that reshaped the nation’s economic and social landscape. This era saw the emergence of industrialization, which brought about major changes in production methods, labor practices, and societal structures.
Economic Impact
Rise of Industrialization:
Technological Advancements: The development of new technologies played a crucial role in the Industrial Revolution. For instance, Eli Whitney’s cotton gin (1793) revolutionized the cotton industry by dramatically increasing the efficiency of cotton processing. This invention not only boosted cotton production but also spurred the growth of the textile industry in the North, linking it to the agricultural economy of the South.
Expansion of Factories: The rise of factory-based production was epitomized by the Lowell Mills in Massachusetts. Founded in the 1820s, these mills employed thousands of young women, known as “Lowell girls,” to work in textile factories. The success of these mills demonstrated the scalability of industrial production and set a precedent for factory work in the U.S.
Growth of Transportation and Infrastructure:
Railroads and Canals: The Erie Canal, completed in 1825, was a major infrastructure project that connected the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes. This canal facilitated the movement of goods and raw materials between the interior of the country and international markets. Similarly, the expansion of the Transcontinental Railroad (completed in 1869) connected the East and West coasts, significantly reducing transportation time and costs, and fostering national economic integration.
Urbanization: Cities like Chicago and New York experienced rapid growth due to industrialization. Chicago, in particular, became a major transportation hub and industrial center, with its location on the railroads and Lake Michigan contributing to its rise. This urban growth led to the expansion of labor markets and increased demand for goods and services.
Economic Expansion:
Market Expansion: The rise of industrial production led to increased market opportunities. For example, the Ford Model T, introduced in 1908, revolutionized the automobile industry. Henry Ford’s use of assembly line production techniques made cars affordable for the average American, expanding the automotive market and stimulating related industries, such as steel and rubber.
Rise of Capitalism: Industrialists such as Andrew Carnegie and John D. Rockefeller exemplify the rise of capitalism during this period. Carnegie’s steel empire and Rockefeller’s Standard Oil Company dominated their respective industries, leading to immense wealth accumulation and influencing the structure of American capitalism.
Labor Market Changes:
Shift from Agriculture: The transition from agricultural to industrial work was evident in the movement of individuals from rural areas to cities. The growth of factories, like the Carnegie Steel Plant in Pittsburgh, created job opportunities that drew labor from agricultural sectors, altering the rural-urban demographic balance.
Industrial Jobs: Workers in factories often faced challenging conditions. For instance, the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in 1911 highlighted the hazardous working conditions in garment factories. The fire, which killed 146 workers, led to increased advocacy for labor safety regulations and the formation of labor unions.
Economic Disparities:
Wealth Concentration: The concentration of wealth among industrialists led to economic disparities. The opulent lifestyles of figures like Rockefeller contrasted sharply with the harsh living conditions of factory workers. This disparity fueled the growth of social reform movements advocating for wealth redistribution and labor rights.
Labor Unions and Strikes: The Pullman Strike of 1894 was a significant labor dispute that reflected the tensions between industrial workers and employers. The strike, which disrupted rail transportation and led to federal intervention, underscored the need for labor reforms and the role of unions in advocating for workers’ rights.
Social Impact
Urbanization and Living Conditions:
Rapid Growth of Cities: The expansion of cities due to industrialization led to both opportunities and challenges. In New York City, neighborhoods like Five Points became notorious for overcrowded and unsanitary conditions, reflecting the difficulties faced by rapidly growing urban populations.
Living Conditions: The rise of industrial cities often resulted in poor living conditions for workers. For example, tenement housing in cities like New York was often cramped and lacked proper sanitation facilities, leading to public health concerns and efforts to reform urban living standards.
Labor Conditions:
Working Hours and Safety: Factory work frequently involved long hours and dangerous conditions. The Molly Maguires, a secret society of Irish-American coal miners, organized strikes in the 1870s to protest unsafe working conditions and low wages in the coal mining industry, illustrating the broader labor struggles of the period.
Labor Reforms: The movement for labor reforms gained momentum following events like the Haymarket Riot of 1886, which was a response to demands for an eight-hour workday. This riot, combined with other labor struggles, led to the eventual establishment of labor laws and better working conditions.
Social Mobility:
Opportunities for Advancement: Despite challenges, industrialization created pathways for social mobility. The story of Andrew Carnegie, who rose from poverty to become a leading industrialist, exemplifies how individuals could achieve significant economic success through hard work and innovation.
Educational Advancements: The need for skilled workers led to increased emphasis on education and vocational training. Institutions like the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), founded in 1861, played a crucial role in advancing technical education and supporting the growing industrial economy.
Family and Gender Roles:
Changing Dynamics: The involvement of women in industrial work was exemplified by the women employed in factories like the Lowell Mills. This shift contributed to early feminist movements and the push for women’s suffrage, reflecting changing gender roles in American society.
Impact on Women: The labor contributions of women in factories and other industries laid the groundwork for the women’s rights movement. Figures like Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton emerged as prominent advocates for women’s rights, including suffrage and labor reform.
Cultural Shifts:
Consumer Culture: The mass production of goods led to the development of a consumer culture. The proliferation of products like automobiles, appliances, and household goods transformed American lifestyles and consumer habits.
Social Movements: The social changes brought about by industrialization led to the rise of various reform movements. The Progressive Era saw reforms aimed at addressing social inequalities, improving labor conditions, and regulating business practices.
Regional Disparities:
- North vs. South: Industrialization had different impacts on various regions of the U.S. The North experienced rapid industrial growth, while the South remained predominantly agrarian. This regional disparity contributed to economic and social tensions, which were evident in events like the Civil War and its aftermath.
Conclusion
It ushered in technological innovations, economic growth, and changes in labor practices, while also highlighting issues of inequality and labor rights. The legacy of the Industrial Revolution continues to influence American society and economy, shaping modern industrial practices, labor laws, and social policies.
The Industrial Revolution in Germany and Russia: Impact on Society and Economy
The Industrial Revolution, which began in Great Britain in the late 18th century, spread across Europe throughout the 19th century, profoundly impacting nations such as Germany and Russia. Both countries experienced the effects of industrialization differently, shaped by their unique political, economic, and social contexts.
Industrial Revolution in Germany
Background and Early Developments:
Pre-Industrial Germany: Before the Industrial Revolution, the German states were fragmented into numerous small principalities and territories, each with its own economic and trade policies. This fragmentation initially hindered large-scale industrial development.
Zollverein (Customs Union): One of the most significant factors in Germany’s industrialization was the formation of the Zollverein (Customs Union) in 1834. This economic union, established under Prussian leadership, aimed to remove internal tariffs and create a single economic area by unifying the various German states under a common trade policy.
Economic Integration: The Zollverein facilitated the free flow of goods and resources across state boundaries, promoting industrial growth. For example, the removal of internal tariffs enabled raw materials such as coal and iron to be transported more efficiently, which was crucial for industries like steel and machinery.
Market Expansion: The creation of a unified market encouraged investment in industrial infrastructure and technology. Cities such as Ruhr Valley became industrial hubs, known for coal mining and steel production. The region’s industrialization was accelerated by the Zollverein’s policies, which also contributed to the growth of railways and communication networks.
Economic Impact:
Industrial Growth: The removal of trade barriers and the integration of German states into a single market spurred significant industrial growth. For example, Friedrich Krupp established a steel manufacturing company in Essen, which became a leading producer of steel and armaments, showcasing the success of industrial ventures facilitated by the Zollverein.
Technological Advancements: The industrial boom led to advancements in technology and production methods. Carl Benz, for instance, developed the first gasoline-powered automobile in 1885, which revolutionized transportation and exemplified the innovative spirit fostered by Germany’s industrial expansion.
Social Impact:
Urbanization: The rapid industrialization led to significant urbanization, with cities like Berlin, Düsseldorf, and Leipzig expanding rapidly as industrial centers. This urban growth brought about both opportunities and challenges, including overcrowded living conditions and the rise of a working class.
Labor Conditions: Industrial work often involved long hours and hazardous conditions. Workers in factories, such as those in the textile industry, faced poor working conditions, which eventually led to the formation of labor unions and social reform movements advocating for better labor standards.
Social Changes: The economic prosperity generated by industrialization contributed to the rise of a middle class and shifts in social hierarchies. Industrialists and entrepreneurs gained prominence, while the traditional aristocracy experienced a relative decline in influence.
Industrial Revolution in Russia
Background and Early Developments:
Late Industrialization: Unlike Western Europe, Russia began industrializing later due to its vast size, feudal social structure, and political conservatism. The major push for industrialization occurred in the late 19th and early 20th centuries under the reign of Tsar Alexander III and his successor Nicholas II.
State-Driven Industrialization: The Russian government played a significant role in industrialization by investing in infrastructure and encouraging foreign investment. For example, the construction of the Trans-Siberian Railway, completed in 1916, connected the European part of Russia with the far east, facilitating resource extraction and trade.
Economic Impact:
Industrial Expansion: Major industries such as steel and oil saw significant growth. The Nobel Brothers established an oil industry in Baku, which became one of the world’s leading oil-producing regions, contributing to Russia’s economic development and integration into the global economy.
Economic Disparities: Despite industrial growth, Russia experienced significant regional disparities. The industrialized western regions, such as St. Petersburg and Moscow, contrasted sharply with the largely agrarian and underdeveloped eastern regions, leading to economic imbalances and social tensions.
Social Impact:
Urbanization and Labor: Rapid industrialization led to urban growth and the expansion of a working class. Cities like St. Petersburg and Moscow saw an influx of workers seeking employment in factories. This urban migration resulted in overcrowded living conditions and led to social unrest, exemplified by the 1905 Russian Revolution, which was partly driven by worker dissatisfaction.
Social Reforms and Movements: The harsh realities of industrial labor conditions spurred social movements and reforms. The October Revolution of 1917, which led to the Bolshevik takeover, was influenced by the growing discontent among workers and peasants. The new Soviet government introduced various reforms aimed at improving labor conditions and redistributing wealth.
Impact on Traditional Structures: Industrialization contributed to the weakening of the feudal social structure and the rise of a more modern class system. The traditional landed aristocracy lost its prominence, while new industrial elites emerged, leading to significant shifts in social hierarchies.
Challenges and Setbacks:
Resistance to Change: In both Germany and Russia, industrialization faced resistance from various quarters. In Russia, the transition to a modern industrial economy was impeded by traditionalists and the remnants of the feudal system, which slowed the pace of industrialization compared to Western Europe.
Economic Crises: Both nations faced economic challenges during their industrialization. Germany’s rapid growth led to economic fluctuations and crises, while Russia’s late industrialization meant it struggled with infrastructural and logistical issues, impacting its overall economic stability.
Conclusion
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on Germany and Russia, shaping their economic and social landscapes in distinct ways. In Germany, the Zollverein played a pivotal role in facilitating industrial growth and economic integration, leading to significant technological advancements and urbanization. In contrast, Russia’s state-driven approach to industrialization led to a more uneven development, with substantial impacts on its labor force and social structure.
Both countries experienced substantial changes due to industrialization, including economic growth, urbanization, and shifts in social hierarchies. However, they also faced challenges, such as economic disparities and social unrest, which reflected the complex nature of industrial transformation.
The French Revolution: A Turning Point in History
Old Regime France and the Ancien Régime
Before the French Revolution, France was entrenched in a rigid social and political structure known as the Ancien Régime. This period, spanning from the late 16th century to 1789, was characterized by absolute monarchy, a feudal social hierarchy, and a deeply entrenched class system.
The society was divided into three estates: the First Estate (clergy), the Second Estate (nobility), and the Third Estate (commoners), which comprised the vast majority of the population. The First and Second Estates enjoyed significant privileges, including tax exemptions, while the Third Estate bore the brunt of taxation and had minimal political power.

The Three Estates of the Ancient Regime
The social structure of France under the Ancient Regime was rigidly hierarchical and divided into three distinct estates. This division shaped the social, political, and economic landscape of pre-revolutionary France, contributing significantly to the tensions that would eventually lead to the French Revolution.
1. The First Estate: The Clergy
Composition and Role: The First Estate comprised the clergy of the Roman Catholic Church. This estate was divided into two main categories:
- The Higher Clergy: This included bishops, archbishops, and abbots who were often from noble families and enjoyed significant wealth and influence. They held substantial power both in religious and secular affairs.
- The Lower Clergy: This group included parish priests, monks, and nuns. Though they were generally less wealthy and powerful compared to the higher clergy, they played a crucial role in local communities and were responsible for pastoral care.
Privileges and Responsibilities:
- Privileges: The clergy were exempt from most taxes, including the taille (a direct tax on land), and received a substantial income from tithes (a religious tax of about 10% of parishioners’ produce or income). They also had significant political influence, with many clergy members holding seats in the Estates-General.
- Responsibilities: In addition to their religious duties, the clergy were expected to provide social services, such as education and charity. They also acted as a link between the monarchy and the people, although their often luxurious lifestyles led to criticism and resentment among the common people.
2. The Second Estate: The Nobility
Composition and Role: The Second Estate consisted of the nobility, which was divided into two main categories:
- The Nobles of the Sword: This traditional nobility traced their lineage back to the medieval period and were associated with military and feudal roles. They held large estates and were often landowners with significant influence in local and national affairs.
- The Nobles of the Robe: This group included individuals who gained noble status through their roles in administrative or judicial positions, often purchased or bestowed as a reward for service. They were involved in legal and bureaucratic functions and had a more modern approach compared to the traditional nobility.
Privileges and Responsibilities:
- Privileges: The nobility enjoyed numerous privileges, including exemption from most taxes (such as the taille), exclusive rights to certain positions and titles, and significant legal and social advantages. They also had their own courts and were often exempt from many laws that applied to commoners.
- Responsibilities: Nobles were expected to provide military service to the king and manage their estates. They were also responsible for upholding traditional feudal obligations and often acted as local lords with authority over peasants.
3. The Third Estate: The Commoners
Composition and Role: The Third Estate encompassed the vast majority of the population and was composed of:
- Peasants: The largest subgroup, peasants worked the land and were subject to feudal obligations and taxes. They lived in rural areas and were often economically disadvantaged.
- Urban Workers: This group included artisans, laborers, and tradespeople who lived in towns and cities. They were frequently involved in various trades and faced economic hardship due to fluctuating markets and high living costs.
- Bourgeoisie: The bourgeoisie comprised the wealthier members of the Third Estate, including merchants, industrialists, and professionals such as lawyers and doctors. They were economically influential but lacked the political power enjoyed by the clergy and nobility.
Privileges and Responsibilities:
- Privileges: The Third Estate had few privileges compared to the other two estates. They were subject to heavy taxation, including the taille and various feudal dues, and had limited political power or representation.
- Responsibilities: Members of the Third Estate were responsible for a significant portion of the tax burden and were expected to contribute to the king’s revenue. They also faced various legal and social restrictions that reinforced their lower status in society.
Detailed Account of the Revolution
1789: The Outbreak
The French Revolution began in 1789, fueled by widespread discontent with the Ancien Régime. The immediate trigger was a severe financial crisis, exacerbated by years of costly wars and extravagant spending by the monarchy, notably under King Louis XVI. The economic strain, combined with poor harvests leading to food shortages, caused immense suffering among the common people.
In May 1789, Louis XVI convened the Estates-General to address the financial crisis. However, disagreements over voting procedures led to a crisis. The Third Estate, feeling marginalized, proclaimed itself the National Assembly, signaling a challenge to royal authority. This led to the dramatic event of July 14, 1789, when Parisian revolutionaries stormed the Bastille, a symbol of royal oppression, marking a significant and symbolic moment in the Revolution.
1790-1791: Early Reforms
Following the fall of the Bastille, the National Assembly began implementing radical reforms. The August Decrees abolished feudal privileges, and the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen was adopted in August 1789, proclaiming equality and rights for all citizens. The Civil Constitution of the Clergy, passed in July 1790, restructured the Catholic Church in France and brought it under state control, further intensifying tensions between revolutionaries and traditionalists.
1792: The Republic and War
The year 1792 saw the establishment of the French Republic. The monarchy was abolished in September, and Louis XVI was executed by guillotine in January 1793. This period also saw the beginning of the War of the First Coalition, as revolutionary France faced threats from various European monarchies opposed to the revolution.
1793-1794: The Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (1793-1794) was marked by radical political measures and widespread executions. The Committee of Public Safety, led by figures like Maximilien Robespierre, sought to defend the revolution from internal and external enemies but did so with extreme measures. Thousands were executed, including Queen Marie Antoinette, and dissent was ruthlessly suppressed. The revolutionary government implemented a series of draconian policies aimed at consolidating power and rooting out perceived counter-revolutionaries.
1795-1799: The Directory and the Rise of Napoleon
The Reign of Terror ended with the fall of Robespierre in July 1794. The National Convention, in an attempt to stabilize France, established the Directory, a five-member executive body. However, the Directory was plagued by corruption, inefficiency, and continued instability. Amidst this chaos, a young general named Napoleon Bonaparte rose to prominence. In 1799, Napoleon staged a coup d’état, overthrowing the Directory and establishing himself as First Consul, thus ending the revolution and beginning the Napoleonic era.
Causes of the Revolution
The causes of the French Revolution were multifaceted:
Social Inequality: The rigid class structure entrenched inequality and resentment among the commoners who were burdened with high taxes and minimal rights.
Economic Hardship: France faced a severe financial crisis due to extravagant royal spending, costly wars, and economic mismanagement, leading to widespread poverty and discontent.
Political Inefficiency: The monarchy’s inability to effectively address financial and social issues, coupled with corruption and ineptitude, eroded its legitimacy.
Enlightenment Ideas: The spread of Enlightenment ideas promoting democracy, equality, and human rights influenced public opinion and fueled demands for political reform.
Weak Leadership: King Louis XVI’s indecisiveness and failure to enact necessary reforms contributed significantly to the revolution’s outbreak.
Rise of Constitutional France
After the fall of the monarchy and the establishment of the Republic, France saw attempts to create a stable government based on constitutional principles. The National Convention, which replaced the National Assembly, was responsible for drafting the first republican constitution, the Constitution of 1793. Although this constitution was never fully implemented due to the tumultuous period of the Reign of Terror, it reflected the revolutionaries’ aspirations for a more democratic and egalitarian society.
The National Convention
The National Convention (1792-1795) was a pivotal legislative body during the Revolution. It oversaw the transition from monarchy to republic, abolished the monarchy, and enacted several important reforms, including the secularization of the church and the establishment of the metric system. However, its tenure was marred by internal strife and external threats, which eventually led to the rise of the radical Jacobins and the Reign of Terror.
The Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror, orchestrated by the Committee of Public Safety, was a period of extreme political repression. The revolutionary government, under Robespierre’s leadership, sought to protect the revolution from perceived enemies through mass arrests and executions. The guillotine became a symbol of the period’s brutality, as thousands, including political opponents and alleged conspirators, were executed. The Reign of Terror ended with Robespierre’s execution in July 1794, leading to a more moderate phase of the revolution.
Final Work of the Convention
In its final phase, the National Convention focused on stabilizing France and drafting a new constitution. The Constitution of 1795, also known as the Constitution of the Year III, established the Directory as the executive body, aimed at providing a more balanced government and ending the excesses of the previous period. This constitution marked a shift towards a more conservative and less radical approach, setting the stage for Napoleon Bonaparte’s rise to power and the end of the revolutionary era.
Conclusion
The French Revolution was a transformative period that reshaped France and had profound effects on the global stage. It dismantled centuries of feudal and monarchical rule, introduced new political ideologies, and set the stage for modern democratic systems. Despite its tumultuous course, the revolution’s legacy continues to influence contemporary politics and society.
The Napoleonic Era: A Detailed Account
The Napoleonic Era, spanning from 1799 to 1815, was a period marked by dramatic changes and conflicts that reshaped Europe. It began with Napoleon Bonaparte’s rise to power and ended with his downfall and the subsequent reorganization of European territories.
1. Early Expedition of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte’s military career began to gain prominence in the late 18th century. His early expeditions, particularly in the Italian campaigns, showcased his strategic brilliance. In 1796, as a young general, Napoleon led the French Army of Italy to a series of victories against the Austrians and their allies. His success in Italy, marked by the capture of significant territories and the signing of the Treaty of Campo Formio in 1797, elevated his reputation and established him as a leading figure in French politics.
2. Egypt’s Campaign
In 1798, Napoleon embarked on an ambitious campaign to Egypt, aiming to undermine British interests in the region and establish a French presence in the Middle East. The campaign began with a successful landing and initial victories, including the Battle of the Pyramids. However, the expedition faced significant challenges.
The French fleet was destroyed by the British at the Battle of the Nile, cutting off Napoleon’s supply lines. Despite these setbacks, Napoleon’s exploration of Egypt’s ancient history and his attempts to integrate into Egyptian society bolstered his image as a visionary leader. The campaign ended with Napoleon’s return to France in 1799, leaving his forces behind.
3. Fall of the Directory
The French Directory, which had governed France since 1795, faced growing instability and corruption. By 1799, the government was increasingly ineffective in dealing with internal and external problems. Discontent among various factions and economic difficulties weakened the Directory’s authority.
Napoleon, returning from Egypt, capitalized on this discontent. On November 9, 1799 (18 Brumaire in the Revolutionary calendar), Napoleon staged a coup d’état, overthrowing the Directory and establishing the Consulate, with himself as First Consul, effectively ending the French Revolution and beginning a new phase of French history.
4. New Constitution of France Under Napoleon
In December 1799, Napoleon introduced a new constitution, known as the Constitution of the Year VIII. This constitution established the Consulate, with Napoleon as First Consul holding substantial executive powers. The new government was designed to provide stability and order, replacing the chaotic and corrupt Directory. The constitution centralized authority and allowed Napoleon to control the military, appoint officials, and influence legislation, effectively consolidating his power.
5. Foreign Campaign Under Consulate
Under the Consulate, Napoleon sought to expand French influence and secure France’s position in Europe. Key foreign campaigns included:
- The War of the Second Coalition (1798-1801): Napoleon negotiated the Treaty of Lunéville with Austria in 1801, which secured French gains and ended the war.
- The Treaty of Amiens (1802): This treaty temporarily ended hostilities between France and Britain, allowing Napoleon to focus on internal reforms and consolidation of power.
6. Reforms by Napoleon
Napoleon implemented a series of significant reforms aimed at stabilizing and modernizing France:
- Legal Reforms: The Napoleonic Code (or Civil Code) of 1804 standardized and codified French law, emphasizing equality before the law, property rights, and civil liberties.
- Administrative Reforms: Napoleon reorganized the administrative structure, creating a more centralized and efficient government. He established a network of prefects to oversee local administration.
- Educational Reforms: He reformed the education system, founding lycées (secondary schools) to train future leaders and bureaucrats.
- Economic Reforms: Napoleon improved infrastructure, such as roads and bridges, and implemented economic policies to stabilize the currency and promote industry.
7. Why a Constitutional Monarchy?
Napoleon’s rise marked a shift from revolutionary republicanism to a form of autocratic rule underpinned by constitutional principles. While he established himself as Emperor in 1804, he maintained elements of the republican system, such as the Codification of laws and institutional reforms.
This blend of autocracy and constitutionalism was designed to provide stability and legitimacy, appealing to both royalists and revolutionaries. The establishment of the Napoleonic Empire aimed to consolidate power while preserving some revolutionary gains and presenting a stable government to the French people.
8. Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803-1815) were a series of conflicts involving Napoleon’s French Empire and various European coalitions:
- The War of the Third Coalition (1803-1806): Napoleon defeated Austria, Russia, and Britain in a series of battles, culminating in the Battle of Austerlitz in 1805.
- The War of the Fourth Coalition (1806-1807): Napoleon’s victories, including the Battle of Jena-Auerstedt, led to the Treaty of Tilsit with Prussia and Russia.
- The Peninsular War (1808-1814): Napoleon’s attempt to enforce the Continental System and replace the Spanish monarch led to a protracted and costly conflict in Spain.
- The Russian Campaign (1812): Napoleon’s invasion of Russia ended in disaster, with the Grande Armée suffering massive losses due to the harsh winter and Russian tactics.
- The War of the Sixth Coalition (1813-1814): Following the Russian campaign, a coalition of European powers defeated Napoleon in the Battle of Leipzig. Napoleon was forced to abdicate in 1814 and was exiled to Elba.
9. Decline of Napoleon
Napoleon’s decline began with the failed Russian campaign of 1812 and subsequent defeats. After his forced abdication in 1814, he was exiled to the island of Elba.
In March 1815, he escaped and returned to France, initiating the Hundred Days. However, his final defeat at the Battle of Waterloo on June 18, 1815, by the British-led coalition forces under the Duke of Wellington and Prussian forces led by Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, marked the end of his rule. Napoleon was then exiled to Saint Helena, a remote island in the South Atlantic, where he died in 1821.
10. The Congress of Vienna, 1815
The Congress of Vienna, held from September 1814 to June 1815, was a diplomatic conference aimed at reordering Europe after Napoleon’s defeat. Key objectives included:
- Restoring Balance of Power: The congress sought to restore the balance of power in Europe to prevent any single nation from dominating.
- Restoring Monarchies: The principle of legitimacy was emphasized, restoring pre-revolutionary monarchies and re-establishing the Bourbon monarchy in France.
- Redrawing Boundaries: European borders were redrawn to stabilize the continent, with significant changes to the territories of France, Prussia, Austria, and other countries.
11. Concert of Europe
The Concert of Europe was a system of international relations established after the Congress of Vienna to maintain the balance of power and prevent future large-scale conflicts. Key features included:
- Regular Meetings: The major powers—Austria, Britain, Prussia, and Russia—held regular meetings to discuss and resolve diplomatic issues.
- Collective Security: The Concert aimed to address and manage conflicts diplomatically, using collective action if necessary to maintain peace.
- Intervention: The system allowed for intervention in revolutionary movements and internal conflicts to preserve the established order and stability.
Conclusion
The Napoleonic Era was a period of significant upheaval and transformation. Napoleon Bonaparte’s rise and fall reshaped Europe, influencing political structures, legal systems, and international relations. His legacy is complex, blending military genius with autocratic rule, and his impact continued to resonate through the subsequent Congress of Vienna and the Concert of Europe, which sought to manage the legacy of his era and restore stability to the continent.
INTRODUCTION
The American Revolutionary War (1775-83) was a conflict between Great Britain and the thirteen British colonies in North America. This war arose from the deteriorating conditions faced by the American colonists under British rule.
The roots of the American Revolution can be traced back to 1763, when British leaders began to intensify their imperial ambitions. This shift disrupted the previously harmonious relationship between Britain and its North American colonies. The British land policy, which restricted settlement in the West, frustrated the colonists. The most significant issue was the need for revenue to support the empire, which led to stringent taxation measures. The Sugar Act, Stamp Act, and Townshend Acts were all attempts to raise funds rather than regulate trade, and they met with increasing resistance in the colonies.
Tensions further escalated after the Parliament passed the Coercive Acts and the First Continental Congress initiated steps toward independence from Britain. The path to independence was marked by a protracted and intense conflict. Ultimately, after a series of political, social, and military struggles, America secured its independence in the late 18th century, leading to the formation of the United States of America. However, the journey was far from straightforward.
Further discord arose between the Northern and Southern states over issues of slavery and state sovereignty, culminating in the Civil War (1861-65). The outcome of this conflict was the abolition of slavery and the reunification of the United States.
In summary, the American Revolution had a profound global impact. It influenced liberal thought worldwide and inspired further movements against oppression.
Thirteen British Colonies in North America The American Revolution (1775-83), also known as the United States War of Independence or the American Revolutionary War, was a pivotal event resulting from the repressive policies of Britain, such as Mercantilism and excessive taxation, imposed on its North American colonies, particularly in the latter half of the 18th century.
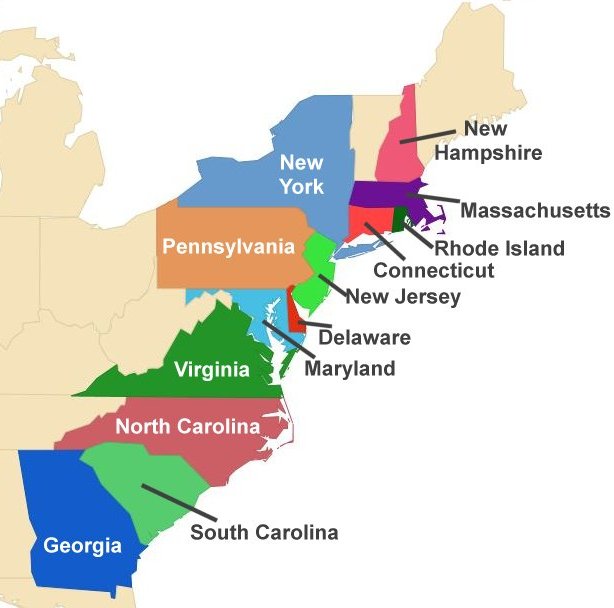
The thirteen colonies of Great Britain (New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia) rebelled during the American Revolutionary War primarily over issues of representation, local laws, and taxation. These colonies united to form the United States of America, which was internationally recognized with the signing of the Treaty of Paris on September 3, 1783.
Prelude European powers such as the French, Spanish, Dutch, and Russians ventured into the Americas to expand their wealth and influence. Among the earliest European settlers were the Spanish, who were the first to explore and settle parts of what is now the United States.
Britain in the 16th and 17th Centuries In the 16th century, England experienced significant upheaval. Landowners preferred raising sheep for wool over farming, leading to food shortages and unemployment among agricultural workers. Great Britain sought to establish colonies in the Americas to expand its empire and counter Spanish influence. The British aimed to discover wealth, create jobs, and establish trade ports.
This period also marked the age of Mercantilism, a competitive economic philosophy that drove European nations to acquire colonies. English colonies in North America were primarily business ventures, designed to generate profits and provide an outlet for England’s surplus population, while offering more religious freedom than England itself.
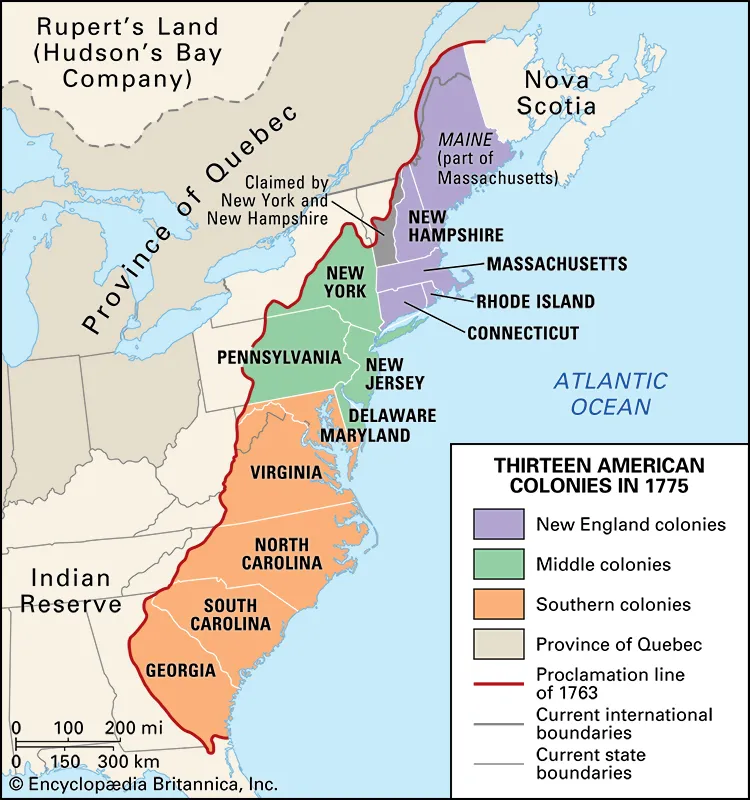
Establishment of British Colonialism in America In 1607, the Virginia Company of London established the first permanent English settlement in North America at Jamestown, Virginia. Operating under a royal charter from King James I, the settlers were assured of liberties similar to those enjoyed in England. Over time, more colonies were established, which were eventually categorized into three regions: New England (Connecticut, Massachusetts Bay, New Hampshire, Rhode Island), the Middle Colonies (Delaware, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania), and the Southern Colonies (Georgia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia).
Relation between Britain and its American Colonies before the 1760s By 1760, the Kingdom of Great Britain had unified England and Scotland, and its American colonies had flourished into thirteen thriving entities. These colonies had strong cultural, economic, and political ties to Britain, and each enjoyed a degree of self-governance.
Seven Years’ War (1756-63) The Seven Years’ War (1756-63), known in America as the French and Indian War, was a global conflict between Great Britain and its allies and France and its allies. French expansion into the Ohio River Valley led to conflicts with British colonies. After a series of defeats, British Prime Minister William Pitt borrowed heavily to finance an expanded war effort. By 1760, the British had expelled the French from Canada and defeated their allies in Europe, securing most of France’s North American territories.
Aftermath of the Seven Years’ War Geo-Political and Financial Troubles: The end of the war left Britain with significant geopolitical and financial challenges. Britain had to govern and protect extensive new territories, including Canada and areas east of the Mississippi River, which included many indigenous and French-speaking populations. Additionally, maintaining control over East and West Florida, acquired from Spain, posed further challenges.
Britain’s Attitudinal Change toward its American Colonies: The war’s conclusion led to a shift in British attitudes toward the American colonies. The British government struggled to get the colonial legislatures to contribute adequately to war expenses. With the French threat eliminated, American colonists questioned the need for a British military presence in North America.
Tussle with the Indians Living in ‘New France’: After the war, British settlers began moving into lands previously controlled by the French, leading to conflicts with Native American tribes. The British ceased the practice of gift-giving to Native American leaders, which had been a means of maintaining good relations. This led to Pontiac’s Rebellion in 1763, where Ottawa leader Pontiac led a revolt against British forces and settlers. Although the conflict ended in 1764, it influenced Britain’s decision to keep a standing army in America.
Causes of Revolt Against the British
The American Revolutionary War was not triggered by a single event but was a culmination of grievances regarding how Great Britain treated its colonies versus how the colonies felt they should be treated.
The British aimed to extract as much revenue as possible from the thirteen North American colonies. They enacted various laws that benefited only Britain and not the colonies, creating a sense of unfairness. The American colonists were neither granted the same rights as British citizens nor given representation in the British Parliament to voice their concerns. This disparity led the Americans to demand equal rights, echoing the rallying cry of “No Taxation Without Representation.” The discontent and protests of the colonists were central to the causes of the American Revolutionary War.
General Causes Leading to the Revolution:
Excessive Taxation Without Parliamentary Representation: The lack of representation in the British Parliament combined with burdensome taxes on items like molasses, paper, sugar, and tea spurred the colonists to oppose British rule, rallying around the slogan “No Taxation Without Representation.”
Restrictions on Free Trade: British laws prevented the Americans from developing their industries and restricted trade. Colonists could only export certain raw materials to Britain and faced heavy duties on non-British imports. Even when trade with other nations was permitted, it had to pass through England, adhering to the principles of Mercantilism.
Unrestricted Search and Seizure: British officers were granted ‘Writs of Assistance,’ allowing them to search any residence or building without notice or oversight. This policy was widely abused and later inspired the Fourth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
Control of Criminal Justice System: Distrust of colonial authorities led the British government to deny colonists the right to jury trials, placing verdicts and punishments under the control of British-appointed judges. These judges were selected, paid, and supervised by British authorities rather than colonial ones.
Destruction of Local Self-Government: British efforts to undermine locally elected governments in the colonies thwarted attempts at self-governance. Even areas unrelated to colonial administration faced interference.
Extraneous Executive Powers: The British Parliament wielded the ‘Bills of Attainder,’ which allowed it to declare individuals guilty and impose penalties without a trial. This draconian measure was used to suppress dissent.
Impunity for British Officials: British officials often enjoyed immunity from consequences for corrupt or abusive behavior. A notable example was the Boston Massacre trial, where eight British soldiers were defended by John Adams, resulting in the acquittal of six. British leaders sought to pass laws ensuring that British officers accused of crimes were tried in England, where securing witnesses would be difficult.
Forced Quartering of Soldiers: Colonists were required to house British soldiers in their homes, a policy that became especially contentious after the Boston Massacre. This led to the adoption of the Third Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, which prohibits the forced quartering of soldiers.
Role of Enlightenment Thinkers
The Enlightenment, with its emphasis on rational change and improvement of humanity, profoundly influenced both the American and French Revolutions. Enlightenment thinkers challenged traditional authority and promoted ideas such as freedom of speech, equality, freedom of the press, and religious tolerance. Concepts like natural rights and governmental structure were derived from Enlightenment philosophy, shaping colonial and modern American governance.
Key figures such as Thomas Jefferson were significantly influenced by Enlightenment principles. These ideas formed the foundation for pivotal documents like the Declaration of Independence and the U.S. Constitution.
John Locke: John Locke introduced the idea of ‘Enlightened Self-Interest,’ suggesting that individuals are rational and capable of seeking the greater good. Locke believed that a ruler’s authority comes from the consent of the governed and that people have natural rights to life, liberty, and property. If a government fails to protect these rights, citizens have the right to overthrow it. This notion greatly influenced Thomas Jefferson in drafting the Declaration of Independence. Locke’s ideas on checks and balances also contributed to the framework of the U.S. Constitution.
Thomas Paine: In January 1776, Thomas Paine published “Common Sense,” a pamphlet advocating for American independence. Paine argued for the superiority of republican government over monarchy and promoted the idea of equal rights for all citizens. His straightforward approach helped galvanize public support for independence.
Benjamin Franklin: Benjamin Franklin played a crucial role in shaping the new American government. He frequently traveled between the colonies and Europe, fostering an exchange of ideas. Franklin was a key figure in drafting the Declaration of Independence, negotiating the Treaty of Paris in 1783, and contributing to the U.S. Constitution as a delegate in 1787.
Montesquieu: Montesquieu, along with Voltaire and Rousseau, was instrumental in promoting democratic ideas. In “The Spirit of Laws,” Montesquieu expanded on Locke’s theories by advocating for the separation of powers and the division of state functions, which became fundamental principles in American governance.
Major Events
The American Revolution, originating from political dissent in the thirteen colonies against the British Empire, culminated in the establishment of the United States as an independent nation. Here are some of the pivotal events that shaped this revolutionary period:
Proclamation of 1763
In October 1763, King George III issued the Proclamation of 1763 after Great Britain’s acquisition of French territories in North America post-Seven Years War. This decree prohibited colonial expansion west of the Appalachian Mountains and required settlers already beyond this line to return east. It invalidated land grants awarded to American veterans and was intended to manage the newly acquired lands and mitigate conflict with Native Americans. The proclamation, though not intended to be permanent, incensed colonists, particularly wealthy speculators who had invested heavily in land companies expecting to profit from western expansion.
Stamp Act, 1765
Passed by the British Parliament in 1765, the Stamp Act was the first direct tax imposed on the colonies. It mandated that all legal documents, including newspapers, contracts, and even playing cards, bear a tax stamp. This tax aimed to cover the costs of British troops in America and reduce the national debt incurred from the Seven Years’ War. The lack of representation in Parliament and the direct nature of the tax sparked widespread outrage among the colonists. Under mounting pressure and resistance, the British repealed the Act in 1766, which was seen as a victory for colonial protestors.
Rockingham Declaration and Townshend Duties, 1767
Following the unrest caused by the Stamp Act, the British government, under Prime Minister Rockingham, asserted its authority to legislate for the colonies, emphasizing Parliament’s rights. Concurrently, the Townshend Acts were introduced to levy new duties on imports such as glass, paper, and tea, aimed at funding colonial governors and judges to ensure their loyalty. The colonists responded with a boycott of British goods, leading to heightened tensions and the eventual Boston Massacre of 1770. Although most of the Townshend duties were repealed in 1770, the Tea Tax remained, symbolizing Parliament’s enduring claim over the colonies.
Tea Act of 1773
To assist the struggling East India Company, the British Parliament passed the Tea Act in May 1773. This act allowed the company to sell tea directly to America without the usual duties, making it cheaper than smuggled Dutch tea. The colonists viewed this as a ploy to force them to accept the Townshend tea tax, leading to widespread opposition.
Boston Tea Party, 1773
On December 16, 1773, in an act of defiance, American patriots disguised as Native Americans boarded ships in Boston Harbor and dumped an entire shipment of British East India Company tea into the water. This protest against the tea tax and the perceived monopoly of the East India Company provoked a severe British response, including the punitive Intolerable Acts of 1774.
Intolerable Acts of 1774
In retaliation for the Boston Tea Party, the British Parliament enacted five punitive laws known as the Intolerable Acts. These included the Boston Port Act, which closed Boston Harbor until the lost tea was compensated; the Administration of Justice Act, allowing trials to be moved if deemed unfair; the Massachusetts Government Act, which dismantled local governance; and the Quartering Act, which permitted British soldiers to be housed in private properties. These measures were seen as severe and unjust, further inflaming colonial resistance.
First Continental Congress, 1774
In response to the Intolerable Acts, the First Continental Congress convened in Philadelphia in 1774. Delegates from the Thirteen Colonies met to address colonial grievances and form a unified response. They established the Continental Association to boycott British goods and issued a Declaration of Rights asserting the colonies’ right to self-taxation. The Congress resolved to reconvene in May 1775 to evaluate further action.
American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War, spanning from 1775 to 1783, commenced with the battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775. The conflict arose from escalating tensions between British forces and colonial militias. Provisional governments in various colonies began organizing militias and seizing arms. The war saw significant events such as the seizure of munitions and confrontations between British troops and colonists, leading to a broader conflict. The war’s culmination came with the British surrender and the Treaty of Paris in 1783.
Second Continental Congress, 1775
Reconvened after the initial battles of the revolution, the Second Continental Congress authorized the formation of the Continental Army and appointed George Washington as its commander. This Congress also produced the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776, formalizing the colonies’ separation from Britain and outlining the new nation’s foundational principles.
Treaty of Paris, 1783
The Treaty of Paris officially ended the American Revolutionary War. Britain recognized American independence and ceded territory east of the Mississippi River to the United States, significantly expanding its borders. The treaty also addressed fishing rights, navigation of the Mississippi River, and resolved issues regarding American debts and loyalist property.
Third Philadelphia Convention, 1787
In May 1787, delegates gathered at Philadelphia’s Pennsylvania State House to address the shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation. Instead of amending the existing document, they drafted a new Constitution, which established a federal system with a bicameral legislature, executive, and judicial branches, and implemented a system of checks and balances. On September 17, 1787, the Constitution was signed by 38 of the 41 delegates and required ratification by nine states to become effective.
American Civil War (1861-65)
The American Civil War, a conflict between the United States and eleven Southern states that seceded to form the Confederate States of America, was driven by deep-seated issues including states’ rights and slavery. The war, which lasted from 1861 to 1865, resolved key questions about national unity and slavery, leading to the preservation of the Union and the end of slavery. The war’s conclusion marked a significant transformation in American society and governance.
Consequences of the American Revolution
The American Revolution had profound impacts:
Political Changes: It led to the birth of the United States, a republic with a democratic federal system. The new Constitution, replacing the Articles of Confederation, established a government with a separation of powers and a system of checks and balances.
Geopolitical Changes: France and Spain gained territories, while Britain lost its American colonies and faced increased debt. The revolution contributed to France’s financial crisis, eventually leading to the French Revolution.
Significance: The revolution inspired movements for democracy and independence worldwide. It demonstrated that overthrowing oppressive regimes was possible and influenced the development of democratic principles and republicanism. The ideals of liberty and self-government spread globally, influencing subsequent revolutions and democratic movements.
The American Revolution also set the stage for future social changes, inspiring movements for equality and rights for women, African Americans, and other marginalized groups. The legacy of the revolution continues to shape the principles of freedom and democracy worldwide.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Describe the primary causes of the American Revolution.
Explain the economic, political, and social factors that led to the colonies’ decision to seek independence from Britain.Analyze the impact of the French and Indian War on the relationship between Britain and its American colonies.
Discuss how the outcomes of the war influenced British policies and colonial attitudes.Evaluate the role of propaganda in the American Revolution.
How did figures like Thomas Paine and publications such as Common Sense influence public opinion and revolutionary sentiment?Compare and contrast the strategies and tactics used by the Continental Army and the British Army during the American Revolution.
What were the strengths and weaknesses of each side’s approach to warfare?Examine the significance of the Declaration of Independence.
What were its main arguments, and how did it influence both American and global perceptions of the revolution?Discuss the role of women and minorities in the American Revolution.
How did different groups contribute to the revolutionary cause, and what were the limitations placed upon them?Assess the impact of foreign assistance on the outcome of the American Revolution.
How did support from countries like France, Spain, and the Netherlands influence the war’s outcome?Explain the effects of the Treaty of Paris 1783 on the post-war United States.
What were the main terms of the treaty, and how did it shape the future political and territorial landscape of the new nation?
Unification of Germany and Italy: A Historical Overview
Introduction
The unification of Germany and Italy in the 19th century was a pivotal process in European history. Both nations, previously fragmented into multiple states and principalities, emerged as unified, powerful entities through a series of complex political, military, and diplomatic manoeuvres.
Unification of Germany
1. Early 19th Century – The German Confederation
- Congress of Vienna (1815): After the Napoleonic Wars, the Congress of Vienna established the German Confederation, a loose association of 39 German-speaking states. This confederation replaced the Holy Roman Empire, which had been dissolved in 1806. Despite its name, the Confederation was not a unified nation but a weak and decentralized alliance with no central authority.
2. 1830s-1840s – Rise of Nationalism
- The Vormärz Period (1830s-1840s): During this period, nationalism and liberalism grew in the German states. Intellectuals and activists advocated for a unified Germany, driven by shared language, culture, and economic interests. Key figures included Johann Gottfried Herder and the Brothers Grimm.
3. 1848 – The Revolutions
- Revolutions of 1848: Widespread revolutions across Europe, including the German states, sought to address social, economic, and political grievances. In the German states, the Frankfurt Assembly was convened in 1848 with the aim of creating a unified German nation-state. However, it failed due to lack of support from powerful German princes and the reluctance of Frederick William IV of Prussia to accept the crown offered by the assembly.
4. 1850s – The Role of Prussia
- Otto von Bismarck: Appointed Prime Minister of Prussia in 1862, Bismarck was a key architect of German unification. His Realpolitik approach involved manipulating diplomatic and military conflicts to achieve unification.
5. 1864-1871 – Wars of Unification
Danish War (1864): Prussia allied with Austria and defeated Denmark, gaining control of the duchies of Schleswig and Holstein. This conflict demonstrated Prussia’s military strength and its role in German affairs.
Austro-Prussian War (1866): Bismarck skillfully isolated Austria diplomatically and defeated it in the Austro-Prussian War. The result was the North German Confederation, led by Prussia, which included most northern German states and excluded Austria.
Franco-Prussian War (1870-1871): Bismarck used the conflict with France to rally southern German states to the Prussian cause. The victory over France fostered a sense of nationalism and paved the way for the proclamation of the German Empire.
6. 1871 – Unification
- Proclamation of the German Empire (1871): On January 18, 1871, King Wilhelm I of Prussia was crowned Emperor of the newly unified German Empire in the Hall of Mirrors at Versailles. The unification process was completed with the inclusion of southern German states, creating a powerful, centralized German nation-state.
Impact of German Unification
- Political Impact: The unification established Germany as a major European power with a strong centralized government and a powerful military.
- Economic Impact: The creation of a single German market facilitated economic growth and industrialization.
- Diplomatic Impact: The balance of power in Europe shifted, leading to new alliances and rivalries, particularly with France.
Unification of Italy
1. Early 19th Century – Fragmentation
- The Italian Peninsula: Prior to unification, Italy was divided into several states, including the Kingdom of Sardinia, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, the Papal States, and various duchies and republics. These divisions resulted from centuries of foreign domination and internal fragmentation.
2. 1820s-1840s – Rise of Nationalism
- The Risorgimento Movement: Italian nationalist sentiments began to coalesce in the early 19th century. Key figures like Giuseppe Mazzini advocated for a united Italy through his organization, Young Italy, while others like Count Camillo di Cavour and Giuseppe Garibaldi became prominent leaders in the unification effort.
3. 1848 – Revolutions
- Revolutions of 1848: Similar to Germany, Italy experienced revolutionary uprisings aimed at achieving national unification and liberal reforms. The revolutions failed to achieve full unification, but they laid the groundwork for future efforts.
4. 1850s-1860s – Key Figures and Events
Count Camillo di Cavour: As Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Sardinia (Piedmont), Cavour played a crucial role in the unification process. He sought to unify Italy under the leadership of the Sardinian monarchy and used diplomacy and strategic alliances to advance this goal.
The Crimean War (1853-1856): Sardinia-Piedmont allied with Britain and France in the Crimean War, gaining favor with these major powers. This alliance helped Cavour gain diplomatic support for Italian unification.
The Austro-Sardinian War (1859): Cavour allied with France against Austria, leading to victories at the Battles of Magenta and Solferino. The Treaty of Zurich resulted in the annexation of Lombardy by Sardinia.
5. 1860 – Garibaldi and the Southern Campaign
- Garibaldi’s Expedition of the Thousand: Giuseppe Garibaldi led a volunteer force to conquer the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies in 1860. His campaign was instrumental in unifying southern Italy with the northern states.
6. 1861 – Proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy
- Kingdom of Italy Proclaimed (1861): On March 17, 1861, the Kingdom of Italy was officially proclaimed with Victor Emmanuel II as its first king. However, unification was not yet complete as Rome and Venetia remained outside the new kingdom.
7. 1870 – Completion of Unification
- Capture of Rome (1870): The final act of Italian unification occurred when Italian troops captured Rome from the Papal States, making it the capital of the Kingdom of Italy. This was facilitated by the withdrawal of French troops who had been stationed in Rome to protect the Pope.
Impact of Italian Unification
- Political Impact: Italy became a unified nation-state with a centralized government. However, regional disparities and political challenges persisted.
- Economic Impact: The unification created a single Italian market, but economic development was uneven, with the north advancing more rapidly than the south.
- Diplomatic Impact: Italy’s unification altered the balance of power in Europe, impacting alliances and rivalries.
Questions for Practice
- Discuss the role of Otto von Bismarck in the unification of Germany. How did his policies and strategies contribute to the creation of the German Empire?
- Evaluate the impact of the Revolutions of 1848 on the processes of unification in Germany and Italy. How did these uprisings influence subsequent events?
- Analyze the significance of the Franco-Prussian War in the context of German unification. How did this conflict influence the unification process?
- Compare and contrast the roles of Giuseppe Garibaldi and Count Camillo di Cavour in the Italian unification. What were their respective contributions and strategies?
- Assess the economic and political impacts of the unification of Italy on the Italian peninsula. How did unification address or exacerbate regional disparities?
World War I: A Detailed Overview
Introduction
World War I, also known as the Great War, was a global conflict that lasted from 1914 to 1918. It was characterized by unprecedented levels of destruction and the involvement of numerous nations across multiple continents. The war’s origins lay in a complex web of political, social, and economic factors that had been building up over decades. The conflict reshaped the political landscape of Europe and had far-reaching consequences for the world order.
1. The Steady Rise of Nationalism
Nationalism, the belief in the supremacy of one’s nation over others, was a powerful force in the early 20th century. Nationalist movements sought to unify people with common cultural or ethnic backgrounds and assert their dominance. In Europe, this led to intense rivalries and competition among nations, particularly in regions like the Balkans and Eastern Europe, where various ethnic groups aspired for independence from larger empires.
2. Imperialism
Imperialism, the policy of extending a country’s power and influence through colonization or military force, was another key factor. European powers competed fiercely for colonies and resources around the world. This competition created conflicts and tensions between major powers such as Britain, France, and Germany, further straining international relations and contributing to the outbreak of war.
3. The Growth of Militarism
The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw a significant increase in military expenditure and the development of advanced weaponry. Militarism, the belief in building up strong armed forces to prepare for war, became prevalent among European powers. This arms race not only created a tense atmosphere but also made war more likely as nations were more prepared and willing to resort to military solutions.
4. Tangled Alliances
By the early 20th century, Europe was divided into two major alliance systems: the Triple Entente (comprising Britain, France, and Russia) and the Triple Alliance (including Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). These alliances were meant to provide security but ended up creating a situation where a conflict involving one member could quickly involve all members, escalating regional disputes into a full-scale war.
5. Shifting Alliances Threaten Peace
The shifting nature of alliances further destabilized Europe. Italy, initially part of the Triple Alliance, switched sides to join the Allies in 1915, while other nations like Japan and the United States later joined the conflict. This constant realignment contributed to the instability and uncertainty in international relations leading up to the war.
6. Social Tensions
Social tensions, including class struggles and labor unrest, were prevalent in many countries. The working class, affected by poor working conditions and economic inequality, was increasingly vocal in its demands. The social unrest contributed to the political instability in various nations, further straining the international system.
7. Crisis in the Balkans
The Balkans were a hotspot of nationalist and ethnic tensions. The decline of the Ottoman Empire and the rise of nationalist movements in the region led to frequent conflicts. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in Sarajevo by a Bosnian Serb nationalist in June 1914 was the immediate trigger for the war, highlighting the volatility of the region.

8. A Shot Rings Throughout Europe
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand set off a chain reaction of events. Austria-Hungary’s ultimatum to Serbia and the subsequent mobilization of alliances turned a localized conflict into a broader war. Within weeks, Europe was plunged into a state of war, as the complex alliance system drew in all major powers.
9. The Balkan Issue
The Balkan Issue, involving the struggle for dominance in southeastern Europe, was a significant factor in the outbreak of World War I. The region was a battleground for competing nationalisms and imperial ambitions, which contributed to the tensions that ignited the conflict.
10. Industrialization & Economic Rivalries
Industrialization had transformed economies and militaries, increasing the capacity for warfare. Economic rivalries, particularly between Germany and Britain, fueled competition and conflict. Nations sought to protect and expand their economic interests, which exacerbated tensions and contributed to the outbreak of war.
11. Conflicts in Europe
The initial phase of World War I saw rapid mobilization and the execution of military strategies, including Germany’s Schlieffen Plan. The early conflicts included significant battles such as the Battle of the Marne, which halted the German advance into France, and set the stage for prolonged trench warfare.
12. The Alliance System Collapses
As the war progressed, the alliance system began to break down. Countries like Italy and the Ottoman Empire joined the Central Powers, while others like Japan and the United States joined the Allies. This shift further complicated the conflict and prolonged the war.
13. The Schlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan was Germany’s military strategy for a two-front war, aiming to quickly defeat France before turning to fight Russia. The plan involved a rapid invasion of France through Belgium. However, logistical issues and the unexpected resistance from Belgium and the Allies thwarted its success, leading to a protracted and bloody conflict.
14. The Battle on the Eastern Front
The Eastern Front saw large-scale battles between Germany and Austria-Hungary on one side and Russia on the other. Major engagements included the Battle of Tannenberg and the Brusilov Offensive. The vastness of the Eastern Front and the shifting front lines characterized this theater of the war, which was less fortified than the Western Front.
15. Trench Warfare
The Western Front was marked by trench warfare, where soldiers faced horrific conditions in dug-in positions stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss border. The trench system led to a stalemate, with neither side able to make significant territorial gains. The war of attrition resulted in massive casualties and suffering.
16. A Truly Global Conflict
World War I became a global conflict with battles fought not only in Europe but also in Africa, Asia, and the Middle East. Colonies of the warring powers were drawn into the conflict, and the war had significant repercussions on a global scale.
17. The Allies Win the War
By 1918, the Allies had gained the upper hand. Key factors included the entry of the United States into the war, which provided a significant boost to the Allied forces, and the exhaustion and internal problems faced by the Central Powers. The Armistice of November 11, 1918, marked the end of fighting, leading to the eventual peace negotiations.
18. A Flawed Peace
The Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, formally ended the war. It imposed harsh penalties on Germany, including significant territorial losses, military restrictions, and reparations. The treaty was criticized for its punitive nature and failure to address underlying issues, which contributed to future tensions.
| Provision | Details |
|---|---|
| Territorial Losses | – Germany lost significant territories: Alsace-Lorraine to France, Eupen-Malmedy to Belgium, and parts of Upper Silesia to Poland. – The Saar Basin was placed under the administration of the League of Nations. |
| Demilitarization | – The Rhineland was demilitarized and occupied by Allied troops to prevent German militarization in the region. – Germany was prohibited from maintaining an army larger than 100,000 men and from having conscription. |
| Reparations | – Germany was required to pay substantial reparations for war damages, amounting to billions of gold marks. – The exact amount was determined later by the Reparations Commission. |
| War Guilt Clause | – Article 231 placed full blame for the war on Germany and its allies, serving as a basis for demanding reparations. |
| Disarmament | – Germany was required to disarm, limiting its army to a small, professional force. – The navy was restricted to a few ships and no submarines. – The air force was entirely disbanded. |
| Colonial Losses | – Germany’s overseas colonies were ceded to the Allies and turned into mandates under the League of Nations. |
| Political and Economic Provisions | – The Treaty called for the establishment of the League of Nations to maintain peace and prevent future conflicts. – The economic provisions included the loss of Germany’s economic resources and trade territories. |
| Creation of New States | – Several new nations were created or expanded, including Poland, Czechoslovakia, and Yugoslavia. – The Austro-Hungarian Empire was dissolved, leading to the creation of new states. |
| Austro-Hungarian Empire | – The Treaty of St Germain (1919) addressed the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, with new states emerging from its territories. |
| Ottoman Empire | – The Treaty of Sèvres (1920) dealt with the Ottoman Empire, leading to its dissolution and the establishment of modern Turkey. |
19. Treaty of St Germain (1919) and the Treaty of Trianon (1920)
The Treaty of St Germain (1919) and the Treaty of Trianon (1920) were the peace treaties that officially ended the war with Austria and Hungary, respectively. These treaties redrew the map of Central Europe, leading to the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the creation of new states. They also imposed significant territorial and military restrictions on the former empire.
20. Treaty of Sevres with Turkey (1920)
The Treaty of Sevres (1920) dealt with the Ottoman Empire, leading to its dissolution and the loss of its territories. It set the stage for the eventual creation of modern Turkey under the leadership of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, following the Turkish War of Independence.
21. Adopting Wilson’s Fourteenth Point, the Treaty Created a League of Nations
President Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteenth Point called for the establishment of a League of Nations to promote international cooperation and prevent future conflicts. The League was created as part of the Treaty of Versailles, aiming to provide a platform for resolving international disputes peacefully.
22. The Creation of New Nations
The post-war treaties led to the creation of several new nations and the redrawing of national boundaries. This included the establishment of states like Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, and Poland. The new political map of Europe was a direct consequence of the war and the peace settlements.
23. Consequences of World War I
World War I had profound consequences:
- Human Cost: The war caused unprecedented casualties, with millions dead and wounded.
- Political Changes: The collapse of empires (Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman, Russian, and German) and the rise of new political ideologies.
- Economic Impact: The war led to economic disruptions and contributed to the Great Depression.
- Social Changes: The war accelerated social changes, including the role of women in the workforce and shifts in societal norms.
- Political Instability: The Treaty of Versailles and other post-war treaties created resentment and political instability, contributing to the conditions that led to World War II.
Conclusion
World War I was a cataclysmic event that reshaped the global order. Its origins were rooted in a complex mix of nationalism, imperialism, militarism, and shifting alliances. The war’s aftermath, characterized by flawed peace treaties and significant geopolitical changes, set the stage for future conflicts and the evolving landscape of international relations.
Questions for Practice
Analyze the role of nationalism in the buildup to World War I. How did it contribute to the outbreak of the war?
Discuss the impact of imperialism and economic rivalries on the geopolitical tensions leading to World War I.
Evaluate the effectiveness of the Schlieffen Plan. What were its strengths and weaknesses, and how did it affect the course of the war?
Examine the consequences of trench warfare on the Western Front. How did it influence military strategies and the war’s outcome?
Assess the Treaty of Versailles and other post-war treaties. To what extent did they address or exacerbate the issues that led to World War I?
Discuss the creation of new nations after World War I. How did the redrawing of boundaries affect the political landscape of Europe?
Analyze the role of the League of Nations in the post-war period. Did it succeed in its aims to prevent future conflicts?
The League of Nations: An Overview
1. Establishment of the League of Nations
The League of Nations was established in the aftermath of World War I, as part of the Treaty of Versailles, which was signed on June 28, 1919. Its creation aimed to prevent future conflicts and foster international cooperation. The League was formally constituted on January 10, 1920, with the headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland.
2. President Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points
President Woodrow Wilson of the United States played a crucial role in the formation of the League of Nations. His Fourteen Points, outlined in a speech on January 8, 1918, proposed a framework for achieving lasting peace. Key points included:
| Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Point 1 | Open diplomacy and transparent international agreements. |
| Point 2 | Freedom of navigation on the seas. |
| Point 3 | Removal of economic barriers and the establishment of equitable trade conditions. |
| Point 4 | Reduction of armaments to the lowest point consistent with domestic safety. |
| Point 5 | Adjustment of colonial claims based on the interests of both the colonizers and the colonized. |
| Point 6 | Restoration of Russian territories and sovereignty. |
| Point 7 | Restoration of Belgian sovereignty. |
| Point 8 | Restoration of French territories, including Alsace-Lorraine. |
| Point 9 | Adjustment of Italian borders to align with the principle of self-determination. |
| Point 10 | Autonomy for Austria-Hungary’s ethnic groups. |
| Point 11 | Restoration of Balkan states and adjustment of their boundaries. |
| Point 12 | Secure sovereignty for the Turkish people and adjustment of Turkish boundaries. |
| Point 13 | Establishment of an independent Polish state with access to the sea. |
| Point 14 | Formation of a League of Nations to ensure political and territorial integrity. |
3. Britain’s Aim
Britain’s primary aim in supporting the League of Nations was to maintain peace and stability in Europe and to prevent the rise of aggressive powers that could threaten British interests. The British government also sought to promote its imperial interests and safeguard its colonies through collective security mechanisms established by the League.
4. Aims of the League
The League of Nations had several key aims:
| Aim | Description |
|---|---|
| Prevent War | To prevent wars through collective security and disarmament. |
| Promote Peace | To resolve international disputes through negotiation and arbitration. |
| Improve Global Welfare | To address global social and economic issues such as health, labor rights, and education. |
| Protect Minorities | To protect the rights of minorities and ensure fair treatment within nations. |
5. Organs of the League
The League of Nations was structured with several key organs:
| Organ | Description |
|---|---|
| Assembly | The main deliberative body where each member had one vote. It met annually to discuss major issues and make decisions. |
| Council | An executive body responsible for decision-making on pressing issues. It included permanent members (Britain, France, Italy, and Japan) and non-permanent members elected by the Assembly. |
| Secretariat | The administrative arm of the League, responsible for managing day-to-day operations. It was headed by the Secretary-General. |
| International Court of Justice | The judicial organ that settled legal disputes between states and provided advisory opinions on legal questions. |
| Permanent Court of International Justice | Predecessor to the International Court of Justice, it was the League’s principal judicial organ until it was replaced by the ICJ in 1946. |
| Mandates Commission | Monitored the administration of territories under League mandates to ensure they were governed in the interests of their inhabitants. |
6. Achievements of the League of Nations
Despite its eventual failures, the League of Nations achieved several successes:
| Achievement | Details |
|---|---|
| Resolution of Disputes | Successfully mediated disputes between countries, such as the Aaland Islands dispute between Sweden and Finland. |
| Social and Humanitarian Work | Implemented programs to combat diseases, improve labor conditions, and promote education. |
| Refugee Assistance | Assisted in the resettlement and care of refugees, particularly those displaced by conflicts and wars. |
| Establishment of International Norms | Set precedents for international cooperation and the establishment of norms in diplomacy and international law. |
7. Causes for the Failure of the League of Nations
The League of Nations ultimately failed to prevent World War II due to several factors:
| Cause | Details |
|---|---|
| Lack of Enforcement Power | The League lacked the authority to enforce its decisions or impose sanctions effectively. |
| Absence of Major Powers | The United States never joined the League, weakening its influence. Additionally, key powers like Germany and the Soviet Union were either excluded or joined late. |
| Ineffective Council | The League’s decision-making process was often slow and ineffective due to the need for unanimous decisions in the Council and Assembly. |
| Failure to Prevent Aggression | The League failed to act decisively against aggressor nations like Japan, Italy, and Germany, who pursued expansionist policies. |
| Economic and Political Instability | The global economic depression of the 1930s and rising political instability contributed to the League’s ineffectiveness in maintaining peace. |
Additional Information:
The League of Nations was dissolved in April 1946, and its responsibilities were transferred to the newly established United Nations. Despite its shortcomings, the League’s efforts laid the groundwork for international organizations aimed at fostering global cooperation and peace.
Questions for Practice:
Evaluate the impact of President Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points on the establishment of the League of Nations.
Discuss the main objectives of the League of Nations and assess to what extent it achieved these objectives.
Analyze the reasons behind the failure of the League of Nations to prevent the outbreak of World War II.
Compare and contrast the roles and functions of the different organs of the League of Nations.
Examine the achievements of the League of Nations in the context of international diplomacy and humanitarian efforts.
The Russian Revolution: An In-Depth Analysis
Background
Before the Russian Revolution, the Russian Empire was an autocratic state ruled by the Romanov dynasty, which had been in power since the early 17th century. Tsar Nicholas II, who ascended the throne in 1894, led a regime characterized by its absolute authority and a lack of political reforms. The empire was vast, comprising diverse ethnic groups and territories, and was marked by significant social and economic inequalities.
The late 19th and early 20th centuries were periods of considerable upheaval in Russia. The rapid industrialization, coupled with the government’s repressive policies and the influence of revolutionary ideologies, created a volatile environment. The lack of political representation and widespread discontent among various social classes set the stage for the revolutionary movements that would eventually lead to the downfall of the Romanov dynasty and the establishment of the Soviet state.
Political Causes
Several political factors contributed to the Russian Revolution:
Autocratic Rule: Tsar Nicholas II’s rigid adherence to autocracy and his resistance to political reform alienated many segments of Russian society, including the burgeoning middle class and the educated elite.
Repression and Censorship: The Tsarist regime’s suppression of political dissent and its censorship of the press stifled political discourse and further fueled revolutionary sentiments.
Weak Political Institutions: The Russian political system lacked democratic institutions. The Duma, the Russian parliament, was weak and had limited power, which contributed to political instability and dissatisfaction.
Economic Causes
The economic conditions in Russia were also a major catalyst for revolution:
Peasant Poverty: The majority of the population were peasants who lived in dire poverty. Despite some reforms, such as the Emancipation Reform of 1861, which freed the serfs, many peasants continued to suffer from land shortages and heavy debt.
Industrial Discontent: Rapid industrialization led to the growth of a working class that faced harsh working conditions, low wages, and poor living standards. This created a fertile ground for socialist ideas and labor unrest.
Economic Inequality: The economic benefits of industrialization were unevenly distributed, exacerbating the wealth gap between the aristocracy and the common people.
Key People in the Russian Revolution
Several key figures played pivotal roles in the Russian Revolution:
Tsar Nicholas II: The last Emperor of Russia, whose autocratic rule and inability to address the grievances of his people contributed to the revolution.
Vladimir Lenin: The leader of the Bolshevik Party, who played a central role in the October Revolution and the establishment of a communist government in Russia.
Leon Trotsky: A key Bolshevik leader and military strategist who was instrumental in the organization of the Red Army and the Bolshevik victory in the Russian Civil War.
Alexander Kerensky: A prominent figure in the Provisional Government who initially led the government after the February Revolution but was later overthrown by the Bolsheviks.
Rise of Socialist Party
The rise of the socialist party was a critical factor in the Russian Revolution:
Socialist Ideologies: The spread of socialist and Marxist ideas, which advocated for the overthrow of the capitalist system and the establishment of a proletarian state, gained traction among the working class and intellectuals.
Formation of the Bolsheviks: Led by Lenin, the Bolsheviks became the most radical and influential socialist faction, advocating for a revolution to establish a dictatorship of the proletariat.
Popular Support: The Bolsheviks garnered significant support due to their promises of “peace, land, and bread,” which resonated with the war-weary soldiers, land-hungry peasants, and disillusioned workers.
World War I
World War I had a profound impact on Russia:
Military Defeats: Russia suffered significant military defeats on the Eastern Front, which eroded the confidence of the public and military in the Tsarist regime.
Economic Strain: The war placed immense economic strain on Russia, leading to shortages of food and other essentials, which further fueled public discontent.
Political Instability: The war exacerbated the political instability in Russia, with the Tsar’s inability to effectively manage the war effort contributing to the erosion of his authority.
The March Revolution
The March Revolution, also known as the February Revolution, began in March 1917 (Julian calendar), when widespread protests and strikes erupted in Petrograd (now St. Petersburg):
Bread Riots: Protests initially started over bread shortages but quickly escalated into a broader movement against the Tsarist regime.
Soviet Influence: Workers’ and soldiers’ councils, known as Soviets, emerged as significant political forces during the revolution, challenging the authority of the Provisional Government.
Mass Protests: Large-scale protests and strikes paralyzed Petrograd, leading to a loss of control by the government and the military.
The Czar Steps Down
Tsar Nicholas II abdicated on March 15, 1917, ending the Romanov dynasty’s rule:
Abdication: Facing overwhelming pressure from the revolutionaries and the military, Nicholas II abdicated in favor of his brother, who refused the throne, leading to the end of the Tsarist autocracy.
Provisional Government: Following the abdication, a Provisional Government was established to govern Russia until a more permanent solution could be found.
Kerensky’s Provisional Government
The Provisional Government, led by Alexander Kerensky, attempted to steer Russia through a transitional period:
Challenges: The government faced significant challenges, including continued involvement in World War I, economic instability, and growing discontent among the population.
Failed Reforms: Although it introduced some reforms, such as granting civil liberties and preparing for elections, it failed to address the pressing issues of land reform and peace.
Loss of Support: The Provisional Government’s inability to withdraw from World War I and address economic woes led to a loss of support, paving the way for the Bolshevik takeover.
The Bolshevik Revolution
The Bolshevik Revolution, also known as the October Revolution, occurred on October 25, 1917 (Julian calendar):
Overthrow of the Provisional Government: The Bolsheviks, led by Lenin and Trotsky, seized key government institutions and effectively overthrew the Provisional Government in a relatively bloodless coup.
Soviet Control: The Bolsheviks established control over major cities and key institutions, consolidating their power and laying the foundation for a communist state.
The Provisional Government Topples
The fall of the Provisional Government marked the beginning of Bolshevik rule:
Immediate Changes: The new Bolshevik government moved quickly to implement socialist policies, including the nationalization of industry and the redistribution of land.
Political Repression: The Bolsheviks suppressed political opposition and established a one-party state, consolidating their control over the country.
Bolsheviks in Power
Once in power, the Bolsheviks faced numerous challenges and made several significant changes:
Civil War: The Bolsheviks faced opposition from various anti-Bolshevik factions, leading to a civil war between the Red Army (Bolsheviks) and the White Army (anti-Bolsheviks).
Policy Implementation: The Bolsheviks implemented radical policies, including the redistribution of land, the establishment of state control over industry, and the withdrawal from World War I through the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk.
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, signed on March 3, 1918, ended Russia’s involvement in World War I:
Territorial Losses: Russia ceded significant territories, including Ukraine, Belarus, and the Baltic states, to the Central Powers.
Economic Impact: The treaty was controversial and contributed to economic and political instability in Russia, but it allowed the Bolsheviks to focus on consolidating power and addressing internal challenges.
Civil War Rages in Russia
The Russian Civil War (1917-1923) was a conflict between the Red Army (Bolsheviks) and the White Army (anti-Bolsheviks):
Fierce Fighting: The civil war was marked by brutal fighting, with significant casualties and widespread suffering.
Foreign Intervention: Several foreign powers intervened in support of the White Army, further complicating the conflict.
Bolshevik Victory: The Red Army, under the leadership of Trotsky, ultimately emerged victorious, solidifying Bolshevik control over Russia.
Lenin Restores Order
Vladimir Lenin played a crucial role in restoring order and consolidating Bolshevik power:
Centralization: Lenin and the Bolsheviks centralized power and established a new government structure, including the Soviet of People’s Commissars.
Economic Reforms: The government implemented policies such as War Communism and later the New Economic Policy (NEP) to stabilize the economy and address shortages.
Political Repression: The Bolshevik regime used repression, including the Cheka (secret police), to eliminate political opposition and maintain control.
Totalitarianism
The Bolshevik Revolution ultimately led to the establishment of a totalitarian state:
One-Party Rule: The Communist Party established a one-party state, with no tolerance for political dissent.
Control Over Society: The state exerted control over various aspects of life, including the economy, media, and education, to maintain its dominance.
Cult of Personality: Lenin and later leaders, such as Joseph Stalin, cultivated a cult of personality and used propaganda to legitimize their rule.
Global and Indian Inspiration
The Russian Revolution had a profound impact on the world and inspired movements globally, including in India:
Global Influence: The success of the Bolsheviks demonstrated the potential for revolutionary change and inspired leftist movements and anti-colonial struggles around the world. The spread of communist ideology influenced various liberation and socialist movements.
Indian Inspiration: In India, the Russian Revolution provided a model for anti-colonial and revolutionary movements. Leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru and Subhas Chandra Bose were inspired by the Bolshevik example, and the idea of socialism gained prominence in the Indian independence movement.
The Russian Revolution thus not only transformed Russia but also had a lasting influence on global politics and revolutionary movements.
TABLE OF IMPORTANT EVENTS
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|
| 1613 | Romanov Dynasty Established | Michael Romanov is elected Tsar, beginning the Romanov dynasty which ruled Russia until 1917. |
| 1905 | Russo-Japanese War | Russia’s defeat in the war leads to widespread unrest and the 1905 Revolution. |
| 1905 | 1905 Revolution | Series of protests and strikes lead to the creation of the Duma, a legislative body. |
| 1914 | Start of World War I | Russia enters World War I as part of the Allies against the Central Powers. |
| 1915 | Nicholas II Takes Command of the Military | Tsar Nicholas II takes personal command of the Russian military, worsening the war’s domestic impact. |
| 1917 (February) | February Revolution | Protests and strikes in Petrograd lead to the abdication of Tsar Nicholas II and the establishment of a Provisional Government. |
| 1917 (March) | Tsar Nicholas II Abdicates | Nicholas II abdicates, ending over three centuries of Romanov rule. |
| 1917 (April) | Lenin Returns to Russia | Lenin returns from exile, bringing his revolutionary ideas to the forefront. |
| 1917 (June) | Kerensky’s Provisional Government | Alexander Kerensky becomes a key leader in the Provisional Government following the February Revolution. |
| 1917 (October) | October Revolution | The Bolsheviks, led by Lenin, overthrow the Provisional Government in the October Revolution. |
| 1917 (November) | Bolshevik Government Established | The Bolsheviks formally establish control, beginning the Soviet regime. |
| 1918 (March) | Treaty of Brest-Litovsk | The Bolshevik government signs the treaty with Germany, ending Russia’s involvement in World War I. |
| 1918-1921 | Russian Civil War | Conflict between the Red Army (Bolsheviks) and the White Army (anti-Bolshevik forces) ensues. |
| 1921 | New Economic Policy (NEP) Introduced | Lenin introduces NEP to stabilize the economy and recover from the war and civil war’s impact. |
| 1922 | Formation of the Soviet Union | The USSR is officially established, consolidating the power of the Bolshevik regime. |
| 1924 | Death of Lenin | Lenin’s death leads to a power struggle, eventually resulting in Joseph Stalin’s rise to power. |
QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICE
1. Analyze the key political and economic causes that led to the Russian Revolution of 1917. Discuss how these factors contributed to the collapse of Tsarist autocracy.
2. Examine the role of World War I in exacerbating the revolutionary conditions in Russia. How did the war impact the political stability and economic conditions in the country?
3. Discuss the significance of the March Revolution in the context of the Russian Revolution. What were its immediate effects on the political landscape of Russia?
4. Evaluate the effectiveness of Alexander Kerensky’s Provisional Government. What were the major challenges it faced, and why did it fail to sustain its rule?
5. Explain the events and strategies involved in the Bolshevik Revolution of October 1917. How did the Bolsheviks consolidate their power in the immediate aftermath of the revolution?
6. Analyze the impact of the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk on the Russian Revolution and its subsequent civil war. How did the treaty affect Russia’s internal and external policies?
7. Assess the role of key figures such as Vladimir Lenin, Leon Trotsky, and Alexander Kerensky in shaping the course of the Russian Revolution. How did their leadership influence the outcomes of the revolution?
8. Explore the major outcomes of the Russian Civil War and how the Bolshevik regime managed to secure its control over Russia. What were the long-term consequences of the civil war for Russian society?
9. Discuss the transition from the initial revolutionary zeal to the establishment of a totalitarian regime under Lenin and later Stalin. How did the Bolshevik government transform into a totalitarian state?
10. Evaluate the global impact of the Russian Revolution, with a focus on its influence on socialist and anti-colonial movements worldwide. How did the revolution inspire political change in other countries, including India?
11. Critically assess the New Economic Policy (NEP) introduced by Lenin. How did it address the economic problems faced by post-revolutionary Russia, and what were its limitations?
12. Compare and contrast the March Revolution and the October Revolution in terms of their causes, key events, and outcomes. How did each revolution contribute to the eventual establishment of Bolshevik rule?
13. How did the Russian Revolution impact the global balance of power in the early 20th century? Discuss the reactions of major world powers to the Bolshevik seizure of power.
14. Analyze the role of the Bolshevik leadership in the suppression of political opposition during the early years of Soviet rule. What methods were employed to maintain political control?
15. Explore the social and economic changes that occurred in Russia as a result of the Bolshevik Revolution. How did these changes affect different segments of Russian society?
The World Between the Two World Wars
The World from 1919-1923
Following the end of World War I in 1918, the world entered a period of intense transformation and uncertainty. The Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, imposed heavy reparations and territorial losses on Germany, creating economic and political instability that would have far-reaching consequences. The League of Nations was established with the goal of promoting peace and preventing future conflicts, but its effectiveness was limited.
Attempts after World War I to Improve International Relations
In the early 1920s, several international efforts were made to stabilize the global order and improve relations between nations. These efforts were characterized by diplomatic conferences and agreements aimed at fostering cooperation and preventing future conflicts.
Impact of the Genoa Conference (1922)
The Genoa Conference of 1922 was a significant diplomatic meeting aimed at addressing the economic and political instability in Europe. The conference focused on economic recovery and the normalization of relations between Germany and the Allied powers. The negotiations did not yield substantial agreements but set the stage for future diplomatic efforts.
Dawes Plan (1924)
The Dawes Plan was an attempt to resolve the problem of German reparations following World War I. Proposed by American banker Charles G. Dawes, it restructured Germany’s reparations payments, reducing the total amount and extending the payment period. It also provided for a loan to help stabilize the German economy. The plan temporarily alleviated some of Germany’s financial problems and facilitated economic recovery.
Locarno Treaties (1925)
The Locarno Treaties were a series of agreements signed in 1925 aimed at securing the post-World War I borders of Western Europe and improving relations between Germany, France, Belgium, Italy, and Britain. The treaties guaranteed the borders between Germany and France and included provisions for mutual security. The treaties were seen as a positive step toward reconciliation and stability in Europe.
Kellogg-Briand Pact (1928)
The Kellogg-Briand Pact, also known as the Pact of Paris, was an international agreement signed by 15 countries, including the United States and France, condemning war as a means of resolving disputes. The pact sought to promote peaceful resolution of conflicts but lacked enforcement mechanisms and was largely symbolic.
Young Plan (1929)
The Young Plan was a follow-up to the Dawes Plan, further revising the terms of German reparations payments. It aimed to reduce the total amount of reparations and extend the payment period until 1988. The plan was designed to stabilize the German economy further but was overshadowed by the onset of the Great Depression.
New Democracies Are Unstable
The post-World War I period saw the emergence of several new democracies in Europe, including Germany, Austria, and Hungary. These democracies were often unstable due to economic difficulties, political extremism, and the lack of democratic traditions. The instability of these new states contributed to the rise of authoritarian regimes.
Weimar Republic Is Weak
The Weimar Republic, established in Germany after World War I, faced significant challenges, including hyperinflation, political extremism, and economic instability. The republic struggled to establish a stable democratic government and was increasingly undermined by extremist movements on both the left and the right.
The Great Depression
The Great Depression, which began with the stock market crash of 1929, was a global economic crisis that had devastating effects on economies around the world. Unemployment soared, industrial production plummeted, and international trade declined. The Depression exacerbated existing political and economic tensions and contributed to the rise of extremist movements.
A Global Depression
The Great Depression affected countries worldwide, leading to widespread economic hardship. Governments struggled to cope with the economic collapse, and many countries turned to protectionist policies and trade barriers in an attempt to shield their economies. The global nature of the Depression highlighted the interconnectedness of the world economy.
The World Responds to the Crisis
In response to the Great Depression, many governments implemented various measures to address the economic crisis. These included economic stimulus programs, public works projects, and social welfare initiatives. However, the effectiveness of these measures varied, and the Depression persisted throughout the 1930s.
Fascism Rises in Europe
The economic and political instability of the 1920s and 1930s contributed to the rise of fascist regimes in Europe. Fascism, characterized by authoritarianism, nationalism, and the suppression of political opposition, gained traction in countries such as Italy, Germany, and Spain. Fascist leaders promised to restore national pride and address economic woes but often resorted to aggressive and repressive tactics.
World Drifts Toward War
As fascist regimes expanded and pursued aggressive foreign policies, Europe drifted toward another major conflict. The failure of diplomatic efforts and the rise of militaristic and expansionist policies contributed to the growing tensions that would eventually lead to World War II.
Fascist Beliefs and Policies
Fascist ideologies were characterized by extreme nationalism, authoritarianism, and the rejection of democratic principles. Fascist regimes sought to create a centralized, dictatorial state, suppress dissent, and promote national unity through propaganda and state control.
Benito Mussolini (1883–1945)
Benito Mussolini was the founder of Italian Fascism and the leader of the National Fascist Party. He rose to power in Italy in the early 1920s, establishing a totalitarian regime characterized by aggressive nationalism and militarism. Mussolini’s policies aimed to restore Italy’s former glory and expand its territorial influence.
Mussolini as the Dictator
As the dictator of Italy, Mussolini implemented various policies to consolidate his power and promote fascist ideals. He established a totalitarian regime, suppressed political opposition, and pursued aggressive foreign policies. Mussolini’s regime sought to create a new Roman Empire and expand Italy’s influence in Europe and Africa.
Hitler Takes Over
Adolf Hitler, the leader of the National Socialist German Workers’ Party (Nazi Party), rose to power in Germany in the early 1930s. Hitler capitalized on economic distress, political instability, and nationalist sentiments to gain support. In 1933, he was appointed Chancellor of Germany and quickly moved to establish a totalitarian regime.
Ascendency of Nazism
The ascendency of Nazism marked the rise of a totalitarian regime in Germany characterized by extreme nationalism, racism, and militarism. Hitler’s policies led to the persecution of Jews, political opponents, and other minorities, and the regime pursued aggressive expansionist goals that contributed to the outbreak of World War II.
Summary of Important Events
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1919 | Treaty of Versailles | Ended World War I and imposed heavy reparations on Germany. |
| 1922 | Genoa Conference | Diplomatic meeting addressing economic recovery in Europe. |
| 1924 | Dawes Plan | Restructured German reparations payments and provided loans for economic stabilization. |
| 1925 | Locarno Treaties | Agreements securing post-World War I borders and improving relations between Germany and France. |
| 1928 | Kellogg-Briand Pact | International agreement condemning war as a means of resolving disputes. |
| 1929 | Young Plan | Revised German reparations payments further, extending the payment period. |
| 1930s | Great Depression | Global economic crisis with severe impact on economies and societies. |
| 1933 | Hitler Becomes Chancellor | Adolf Hitler rises to power in Germany, establishing a totalitarian regime. |
| 1933 | Nazi Party Ascends | Rise of Nazism in Germany, leading to aggressive policies and the eventual outbreak of World War II. |
Practice Questions
- Discuss the impact of the Treaty of Versailles on the political and economic stability of Europe in the early 20th century.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the Dawes Plan and the Young Plan in addressing Germany’s post-World War I economic issues.
- Analyze the role of the Locarno Treaties in fostering stability in Western Europe.
- How did the Great Depression contribute to the rise of extremist political movements in Europe?
- Assess the significance of the Kellogg-Briand Pact in the context of international diplomacy and its limitations.
- Examine the causes and consequences of the rise of fascism in Italy and Germany.
- Compare and contrast the economic policies of Mussolini and Hitler in their respective fascist regimes.
- Explain how the political and economic conditions of the 1920s and 1930s set the stage for the outbreak of World War II.
World War II: A Comprehensive Overview
World War II, spanning from 1939 to 1945, was the deadliest and most widespread conflict in human history. It involved vast swathes of the globe and a complex array of causes and consequences. Below is a detailed account of the key factors, major events, and the lasting impacts of this monumental conflict.

Factors That Caused the Second World War
Treaty of Versailles (1919): The harsh terms imposed on Germany after World War I created deep-seated resentment and economic hardship. The reparations and territorial losses fueled nationalism and paved the way for aggressive expansionist policies.
Rise of Totalitarian Regimes: The economic instability of the 1920s and 1930s contributed to the rise of totalitarian regimes. Leaders like Adolf Hitler in Germany, Benito Mussolini in Italy, and militarists in Japan exploited the economic crises to gain power and pursue aggressive expansionist policies.
Failure of the League of Nations: The League of Nations, created to prevent future conflicts, failed to enforce its resolutions or prevent aggression. Its inability to address international disputes and conflicts contributed to the outbreak of World War II.
Expansionist Policies: Germany’s invasion of Poland, Italy’s invasion of Ethiopia, and Japan’s invasion of China were direct challenges to the international order and led to widespread conflict.
Appeasement: European powers, particularly Britain and France, initially pursued a policy of appeasement towards Germany, allowing Hitler to annex territories in the hope of avoiding a larger conflict. This policy ultimately emboldened Hitler and contributed to the war’s outbreak.
Hitler’s Role
Adolf Hitler, the Führer of Nazi Germany, played a central role in the outbreak of World War II. His aggressive expansionist policies aimed at overturning the post-World War I settlement, annexing neighboring territories, and establishing a Greater German Empire directly led to the conflict. Key events in his role include:
Reoccupation of the Rhineland (1936): Hitler defied the Treaty of Versailles by remilitarizing the Rhineland, a move that went unchecked by the Allies.
Annexation of Austria (Anschluss, 1938): Hitler annexed Austria into Germany, further expanding German territory.
Munich Agreement (1938): Hitler, along with British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain and French Premier Édouard Daladier, agreed to allow Germany to annex the Sudetenland of Czechoslovakia in exchange for a promise of no further territorial expansion.
Invasion of Poland (1939): The invasion of Poland by Germany on September 1, 1939, triggered the war as Britain and France declared war on Germany.
Germany Sparks a New War in Europe
Germany’s invasion of Poland marked the beginning of World War II in Europe. Using Blitzkrieg tactics—characterized by rapid, coordinated attacks involving infantry, tanks, and air support—Germany quickly overran Polish defenses. This strategy demonstrated the effectiveness of modern mechanized warfare and led to the swift conquest of Poland.
France Battles Back
Following the fall of Poland, Germany turned its attention to Western Europe. The German invasion of France in May 1940 involved a surprise attack through the Ardennes Forest, bypassing the heavily fortified Maginot Line. France was quickly overrun, leading to an armistice and the establishment of the Vichy government.
The War in the Balkans During World War II
The Balkans, a region known for its complex ethnic and political landscape, became a significant theater of conflict during World War II. The strategic importance of the Balkans, coupled with its diverse national interests, made it a focal point for military operations and political maneuvering. This article explores the key events and impact of the War in the Balkans during World War II.
Background
The Balkans had been a region of instability and conflict even before World War II. The area, comprising countries like Greece, Yugoslavia, and Bulgaria, had a history of nationalist strife and political turmoil. The outbreak of World War II saw these tensions exacerbated by the expansionist ambitions of the Axis powers, primarily Germany and Italy.
The Axis Powers’ Expansion
Italy’s Invasion of Albania (April 1939):
- Italy, under Benito Mussolini, invaded Albania in April 1939, marking the beginning of Italian expansion in the Balkans. The occupation aimed to secure Italy’s influence in the region and was part of Mussolini’s broader goal of establishing a New Roman Empire.
Germany’s Strategic Interests:
- The Balkans held significant strategic importance for Germany. The region was a critical pathway to the Soviet Union and a strategic asset for controlling Eastern Europe. Germany’s plans for Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the Soviet Union, necessitated secure southern flanks and access routes through the Balkans.
The German Invasion of Greece and Yugoslavia
Coup in Yugoslavia (March 1941):
- In March 1941, a coup d’état in Yugoslavia overthrew the pro-Axis government of Prince Paul and installed a pro-Allied government under King Peter II. This change was driven by widespread opposition to the Axis powers and the desire to resist German domination.
German Invasion of Yugoslavia (April 1941):
- In response to the coup, Germany launched Operation 25, the invasion of Yugoslavia, on April 6, 1941. The operation was swift and brutal. The Axis forces, including German, Italian, and Hungarian troops, quickly overwhelmed Yugoslav defenses. The country was occupied, and the Axis powers established a puppet state, the Independent State of Croatia, which included parts of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina.
German Invasion of Greece (April 1941):
- Concurrently, Germany invaded Greece to secure its southern flank before launching Operation Barbarossa. The invasion began on April 6, 1941, and, despite fierce resistance from Greek and British Commonwealth forces, Germany achieved a swift victory. Greece was divided between German, Italian, and Bulgarian occupation zones.
The Impact of Axis Occupation
Resistance Movements:
- The occupation of the Balkans saw the rise of various resistance movements. In Greece, the Greek Resistance comprised several factions, including the communist EAM (National Liberation Front) and the royalist EDES (National Republican Greek League). In Yugoslavia, the communist Partisans led by Josip Broz Tito fought against the Axis and the collaborating Ustaše regime, while the Chetniks, led by Draža Mihailović, also engaged in resistance but with varying degrees of collaboration with Axis forces.
Humanitarian Crisis:
- The occupation led to widespread suffering among the civilian population. The Axis powers’ policies, including forced labor, reprisals against resistance activities, and the systematic persecution of Jews, caused significant hardship. The Holocaust saw the deportation and murder of Jewish communities in the region.
Strategic Importance:
- The Balkans’ strategic importance continued throughout the war. The region was a crucial supply route for the Axis powers and a significant front in the conflict between the Axis and Allied forces.
Allied Counteroffensive
Operation Torch (November 1942):
- The Allied invasion of North Africa, known as Operation Torch, was part of a broader strategy to open up a second front against the Axis powers. The success of this operation and subsequent campaigns in North Africa forced the Axis to divert resources and attention away from the Balkans.
Allied Invasion of Italy (July 1943):
- Following the Italian surrender in September 1943, the Allies launched an invasion of Italy, which opened up the Mediterranean front. The resulting Italian Campaign further affected Axis operations in the Balkans, as German forces were stretched thin.
The Balkans Campaign (1944-1945):
- In late 1944 and early 1945, the Allies, supported by local resistance movements, launched a series of offensives to liberate the Balkans. The Soviet Union also contributed to the pressure on Axis forces. The combined efforts led to the liberation of Yugoslavia, Greece, and Albania by the end of the war.
Post-War Consequences
Political Repercussions:
- The post-war period saw the establishment of communist governments in several Balkan countries. In Yugoslavia, Tito’s Partisans emerged as the dominant power, leading to the establishment of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Greece experienced a civil war between communist and royalist forces, eventually leading to a royalist victory and the establishment of a conservative government.
Reparations and Reconstruction:
- The war left a legacy of economic and infrastructural damage in the Balkans. The post-war reconstruction involved rebuilding infrastructure, addressing the humanitarian crisis caused by the war, and integrating the region into the emerging Cold War geopolitical landscape.
Summary of Major Events in the Balkans During World War II
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| April 1939 | Italian Invasion of Albania | Italy expands its influence in the Balkans. |
| March 1941 | Coup in Yugoslavia | Overthrow of pro-Axis government, leading to Axis invasion. |
| April 1941 | German Invasion of Yugoslavia | Swift occupation and establishment of a puppet state. |
| April 1941 | German Invasion of Greece | Greece is divided among Axis powers. |
| November 1942 | Operation Torch | Allied invasion of North Africa, impacting Balkans strategy. |
| July 1943 | Allied Invasion of Italy | Opens up Mediterranean front, affecting Balkan operations. |
| 1944-1945 | Balkans Campaign | Allied and local resistance efforts lead to liberation. |
Effective Leaders
| Country | Leader | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Yugoslavia | Josip Broz Tito | Leader of the Partisans |
| Greece | Georgios Papandreou | Prime Minister and leader of Greek resistance |
| Italy | Benito Mussolini | Dictator of Fascist Italy |
| Germany | Adolf Hitler | Führer of Nazi Germany |
| United Kingdom | Winston Churchill | British Prime Minister |
| United States | Franklin D. Roosevelt | U.S. President, supported Allied strategy |
Impact and Legacy
The War in the Balkans during World War II was marked by intense conflict and significant consequences. The region’s strategic importance, combined with its complex political and ethnic landscape, made it a crucial battleground in the broader context of the global conflict. The war’s impact included:
- Human Cost: The war caused immense suffering, including the Holocaust, widespread civilian casualties, and displacement.
- Political Changes: The post-war period saw the establishment of communist regimes in several Balkan countries, altering the region’s political landscape for decades.
- Strategic Shifts: The liberation of the Balkans contributed to the Allied victory and influenced the post-war balance of power.
The War in the Balkans highlights the interconnected nature of World War II and underscores the importance of the region in the broader context of global conflict and post-war reconstruction.
The Battle of Stalingrad: A Brief Overview
The Battle of Stalingrad, fought between July 17, 1942, and February 2, 1943, was one of the most significant and brutal confrontations of World War II. It marked a turning point in the Eastern Front and is often cited as the most decisive Soviet victory over Nazi Germany.
Background
Strategic Importance:
- Stalingrad (now Volgograd) was a crucial industrial city on the banks of the Volga River, providing strategic significance for both the Axis and Soviet forces. Its capture was intended to secure Germany’s southern flank, protect the oil fields in the Caucasus, and disrupt Soviet supply lines.
The Axis Plan:
- Adolf Hitler aimed to capture Stalingrad to solidify German dominance in the Soviet Union and gain control of the southern Russian territories. The city’s fall was part of Germany’s broader Operation Barbarossa, which sought to achieve a swift victory over the Soviet Union.
Key Phases of the Battle
German Offensive (July – August 1942):
- The German 6th Army, led by General Friedrich Paulus, advanced towards Stalingrad, making significant gains and encircling parts of the city. The Luftwaffe conducted relentless bombing raids, turning much of Stalingrad into ruins.
Soviet Defense (August – November 1942):
- The Soviets, under the command of General Vasily Chuikov, mounted a determined defense despite severe losses. The harsh urban combat, characterized by house-to-house fighting, turned the city into a fortress. Soviet forces utilized every building for defense and launched counterattacks to slow down the German advance.
Operation Uranus (November 1942):
- In response to the growing Soviet resistance, the Soviet High Command executed Operation Uranus, a massive counteroffensive designed to encircle and trap the German 6th Army within Stalingrad. Soviet forces, including General Aleksandr Vasilevsky’s armies, launched a series of coordinated attacks from the north and south, successfully encircling the German forces.
German Surrender (January – February 1943):
- Surrounded and cut off from supplies, the German 6th Army faced dire conditions. Despite Hitler’s orders to hold the position, the encircled German troops, suffering from starvation and freezing temperatures, were forced to surrender on February 2, 1943. The battle ended with the surrender of approximately 91,000 German soldiers, including General Paulus, and marked the complete defeat of the Axis forces in Stalingrad.
Impact and Significance
Turning Point:
- The Battle of Stalingrad marked the first major defeat of the German Army and signaled the beginning of a Soviet offensive that would eventually push the Axis forces back across Eastern Europe. It shifted the momentum of the war in favor of the Allies on the Eastern Front.
Human Cost:
- The battle was one of the deadliest of the war, with estimates of casualties ranging from 1.2 to 2.5 million, including soldiers and civilians. The extreme conditions, heavy bombardment, and brutal combat led to significant loss of life and suffering.
Psychological Impact:
- The victory at Stalingrad was a significant morale booster for the Soviet Union and marked the beginning of the Soviet Union’s push westward. For the Germans, it was a demoralizing defeat that undermined their previously unstoppable momentum and strained their military resources.
Legacy:
- The Battle of Stalingrad remains a symbol of Soviet resilience and military strategy. It demonstrated the effectiveness of urban warfare and the importance of logistical support and strategic planning in modern warfare.
Summary of Key Points
- Dates: July 17, 1942 – February 2, 1943
- Location: Stalingrad, Soviet Union (now Volgograd, Russia)
- Key Figures: General Friedrich Paulus (Germany), General Vasily Chuikov (Soviet Union)
- German Strategy: Capture Stalingrad to secure southern flank and disrupt Soviet supply lines
- Soviet Strategy: Defensive warfare, urban combat, Operation Uranus (counteroffensive)
- Outcome: Soviet victory, encirclement and surrender of German 6th Army
The United States Aids Its Allies
The United States, initially neutral, began providing aid to Allied nations through the Lend-Lease Act of 1941. This policy allowed the U.S. to supply military aid and equipment to Britain, the Soviet Union, China, and other Allied nations. The U.S. formally entered the war after Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941.
Japan Strikes in the Pacific
Japan’s surprise attack on Pearl Harbor led to the U.S. entering the war. Following the attack, Japan rapidly expanded its territorial control across the Pacific, capturing territories such as Hong Kong, Singapore, and the Philippines. The Pacific War saw intense naval and island-hopping campaigns.
The Allies Strike Back
The Allies launched a series of counteroffensives in both Europe and the Pacific. In Europe, the Allies began to push back against German forces with key victories in North Africa and Italy. The D-Day invasion of Normandy (June 6, 1944) was a critical operation that opened a Western Front against the Germans.
The Holocaust Begins
The Holocaust was the systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million Jews by the Nazi regime. It also targeted other groups, including Romani people, disabled individuals, Polish and Soviet civilians, and political dissidents. The genocide was facilitated through concentration and extermination camps.
The Allies Are Victorious
The war in Europe concluded with the unconditional surrender of Germany on May 8, 1945 (V-E Day). In the Pacific, Japan surrendered on August 15, 1945, following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, leading to the end of World War II on September 2, 1945.
Nation-Specific Effects
Germany: The war resulted in the devastation of Germany’s cities, extensive loss of life, and the division of the country into East and West Germany during the Cold War.
Japan: Japan experienced massive destruction from Allied bombings, including the atomic bombings, and was occupied by Allied forces, leading to significant political and economic reforms.
Britain: The UK faced extensive damage to its cities, economic challenges, and a decline in its global influence, leading to the end of its colonial empire.
Soviet Union: The USSR suffered immense casualties and destruction but emerged as a superpower with significant influence in Eastern Europe and the beginning of the Cold War.
United States: The U.S. emerged as a global superpower with increased economic and military influence and played a key role in shaping the post-war world order.
Effects Upon the Non-European World
The war had significant impacts beyond Europe and Asia:
Decolonization: The weakening of European powers accelerated decolonization movements in Africa, Asia, and the Middle East.
Economic Impact: Many non-European countries experienced economic disruptions but also benefited from increased U.S. economic aid and investment.
Global Institutions: The creation of the United Nations aimed to prevent future global conflicts and promote international cooperation.
The Devastation of Europe and Japan
Europe and Japan were left in ruins after the war. Cities were destroyed, economies were shattered, and millions of people were displaced. The rebuilding process was extensive, involving significant international aid, including the Marshall Plan for Europe.
Impact of World War II
World War II fundamentally altered the global balance of power. It led to:
The Cold War: The emergence of the U.S. and the USSR as superpowers and the beginning of the Cold War rivalry.
Creation of the United Nations: An international organization established to promote peace and prevent future conflicts.
Economic and Social Change: The war accelerated technological advances, shifts in global economic power, and social changes, including movements towards greater equality.
The Legacy of World War II
The legacy of World War II is profound:
International Relations: The war reshaped international relations, leading to the establishment of a new world order centered around the U.S. and the USSR.
Human Rights: The horrors of the Holocaust prompted the development of international human rights frameworks and conventions.
Geopolitical Boundaries: The borders and political landscapes of many countries were redrawn, influencing global politics for decades.
| Year | Month/Date | Event |
|---|
| 1939 | September 1 | Germany, under Hitler, invades Poland. Britain and France declare war on Germany two days later. |
| 1940 | – | Rationing begins in the United Kingdom. |
| – | Germany’s ‘Blitzkrieg’ strategy quickly defeats Belgium, the Netherlands, and France. |
| – | Winston Churchill is appointed Prime Minister of Britain. |
| – | The British Expeditionary Force is evacuated from Dunkirk. |
| – | The Battle of Britain ends with a British victory, causing Hitler to delay his invasion plans. |
| 1941 | – | Operation Barbarossa commences as Hitler invades the Soviet Union. |
| – | The Blitz continues, with German bombing raids targeting major British cities. |
| – | Allied forces capture Tobruk in North Africa and repel German assaults. |
| December 7 | Japan launches an attack on Pearl Harbor, prompting the United States to enter the war. |
| 1942 | – | Germany faces setbacks in the battles of Stalingrad and El Alamein. |
| February | Singapore falls to Japanese forces; approximately 25,000 prisoners are taken. |
| June | The American naval victory at the Battle of Midway marks a turning point in the Pacific Theater. |
| – | The mass extermination of Jewish people begins at Auschwitz. |
| 1943 | – | The surrender of German forces at Stalingrad represents their first major defeat. |
| – | The Allied victory in North Africa facilitates the invasion of Italy. |
| – | Italy capitulates, but Germany continues to fight in Italy. |
| – | British and Indian troops engage Japanese forces in Burma. |
| 1944 | – | Allied troops land at Anzio and bomb the Monte Cassino monastery. |
| – | Soviet offensives accelerate in Eastern Europe. |
| June 6 | D-Day: Allied forces land in France, leading to the liberation of Paris in August. |
| – | The US liberates Guam; bombing campaigns target Okinawa and Iwo Jima. |
| 1945 | – | Soviet forces liberate Auschwitz. |
| May 7 | Soviet troops reach Berlin; Hitler commits suicide, and Germany surrenders. |
| April 12 | Harry S. Truman becomes President of the United States following Roosevelt’s death, and Clement Attlee succeeds Churchill. |
| August 14 | Japan surrenders after atomic bombs are dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. |
Tabular Representation of Major Powers and Their Allies
| Allied Powers | Axis Powers |
|---|---|
| United States | Nazi Germany |
| United Kingdom | Italy |
| Soviet Union | Japan |
| France | Hungary |
| China | Romania |
| Canada | Bulgaria |
| Australia | Finland |
Notable Leaders of World War II
| Country | Leader | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Germany | Adolf Hitler | Führer of Nazi Germany |
| United States | Franklin D. Roosevelt | President of the United States |
| United Kingdom | Winston Churchill | Prime Minister |
| Soviet Union | Joseph Stalin | General Secretary of the Communist Party |
| Japan | Emperor Hirohito | Emperor of Japan |
| Italy | Benito Mussolini | Prime Minister and Duce of Fascism |
Practice Questions
- Analyze the main factors that led to the outbreak of World War II. How did these factors contribute to the global scale of the conflict?
- Evaluate Hitler’s role in the escalation of World War II. How did his policies and actions shape the course of the war?
- Describe the key military strategies used by Germany in the early years of World War II. How did these strategies lead to the rapid expansion of German control?
- Discuss the impact of the Battle of Stalingrad on the Eastern Front. How did it influence the subsequent course of the war in Europe?
- Assess the significance of the United States’ entry into World War II. How did American involvement change the dynamics of the conflict?
- Examine the causes and consequences of Japan’s expansion in the Pacific. How did this expansion impact the overall course of the war?
- Analyze the effects of World War II on the global balance of power. How did the war lead to the emergence of the United States and the Soviet Union as superpowers?
- Explore the long-term impacts of World War II on Europe and Japan. How did the war shape the post-war reconstruction and geopolitical landscape?
The Cold War: An Overview
Introduction
The Cold War was a prolonged period of political, military, and ideological tension between the United States and its allies (the Western bloc) and the Soviet Union and its allies (the Eastern bloc) that lasted from the end of World War II until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Unlike traditional wars, the Cold War did not involve direct large-scale military conflict between the two superpowers but was characterized by proxy wars, nuclear arms races, and ideological competition.
Cold War: Causes
The roots of the Cold War lie in the divergent ideologies and interests of the United States and the Soviet Union that became evident as World War II drew to a close. The primary causes include:
- Ideological Differences: Capitalist democracies (led by the U.S.) versus communist totalitarian regimes (led by the USSR).
- Power Vacuums: Post-war Europe and Asia experienced power vacuums, which both superpowers sought to fill.
- Mutual Suspicion: Distrust fueled by each side’s actions during and after WWII, including differing visions for the post-war world order.
- Nuclear Arms Race: Both superpowers sought to outdo each other in nuclear weapons capability, leading to an arms race.
Former Allies Diverge
During WWII, the U.S. and the Soviet Union were allies against the Axis powers. However, their cooperation quickly disintegrated after the war. Disputes over the future of Eastern Europe, differing interpretations of the Yalta Conference agreements, and Stalin’s establishment of communist governments in Eastern Europe heightened tensions. The mutual distrust and conflicting interests set the stage for the Cold War.
The Soviet Union Cages Eastern Europe
Post-WWII, the Soviet Union established control over Eastern Europe through a combination of military power and political manipulation. Stalin imposed communist regimes in countries such as Poland, Hungary, and Czechoslovakia, often through rigged elections and suppression of dissent. This Soviet dominance led to the formation of the Eastern bloc, which became a focal point of Cold War tensions.
United States Counters Soviet Expansion
In response to Soviet expansionism, the United States adopted policies aimed at containing communism. The Truman Doctrine (1947) and the Marshall Plan (1948) were instrumental in providing economic and military aid to European countries resisting communist influence. The creation of NATO in 1949 further solidified the Western bloc’s military alliance against the perceived threat from the Soviet Union.
The Cold War and a Divided World
The world became increasingly polarized into two ideological camps: the capitalist West and the communist East. This division influenced global alliances, international diplomacy, and conflicts. Countries were often forced to choose sides, leading to a series of proxy wars and conflicts in various regions.
Situation in Korea
The Korean War (1950-1953) was a major Cold War conflict that arose from the division of Korea into North and South at the end of WWII. North Korea, supported by the Soviet Union and China, invaded South Korea, prompting U.N. intervention led by the U.S. The war ended in a stalemate, with Korea remaining divided at the 38th parallel, a situation that persists to this day.
War in Vietnam
The Vietnam War (1955-1975) was another significant Cold War conflict. The North, supported by communist allies including the Soviet Union and China, fought against the South, which was supported by the U.S. and its allies. The war ended with the fall of Saigon in 1975, leading to the reunification of Vietnam under communist control.
Case of Cambodia
Cambodia was significantly affected by the Vietnam War. The Khmer Rouge, led by Pol Pot, seized power in 1975, establishing a brutal communist regime. The regime’s radical policies led to the deaths of approximately two million people. The U.S. and other Western nations initially supported anti-communist factions, contributing to the conflict’s complexity.
Confrontations over Developing Nations
The Cold War saw numerous proxy conflicts in developing nations, where the superpowers vied for influence. Examples include U.S. and Soviet support for opposing factions in conflicts in Africa, Latin America, and Asia. These interventions often exacerbated local conflicts and contributed to regional instability.
Situation in Latin America
In Latin America, the Cold War manifested in various forms, including U.S. interventions in countries like Cuba, Chile, and Nicaragua. The Cuban Revolution (1959) and the subsequent Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) were pivotal moments, as the U.S. and USSR confronted each other directly over Cuba’s communist government.
The Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis (October 1962) was a 13-day confrontation between the U.S. and the Soviet Union over Soviet ballistic missiles deployed in Cuba. It is considered the closest the world came to nuclear war. The crisis ended with the USSR agreeing to withdraw missiles from Cuba in exchange for a U.S. promise not to invade the island and a secret agreement to withdraw U.S. missiles from Turkey.
Middle East
The Cold War heavily influenced Middle Eastern geopolitics, with both superpowers seeking to extend their influence. Conflicts such as the Six-Day War (1967) and the Yom Kippur War (1973) were influenced by Cold War dynamics, with the U.S. supporting Israel and the USSR backing various Arab states.
The Iran-Iraq War
The Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988) was another conflict with Cold War implications. Iraq, under Saddam Hussein, received support from Western and Arab nations, while Iran, following the 1979 Islamic Revolution, received support from the Soviet Union. The war had devastating effects on both countries and the wider region.
The Superpowers Face Off in Afghanistan
The Soviet invasion of Afghanistan (1979-1989) was a key Cold War conflict. The U.S. and its allies supported Afghan resistance fighters (Mujahideen) against Soviet forces. The conflict drained Soviet resources and contributed to domestic discontent within the USSR.
Eastern Europe
Throughout the Cold War, Eastern European countries were under Soviet control. The Soviet Union suppressed uprisings and dissent in countries like Hungary (1956) and Czechoslovakia (1968). These events underscored the rigidity of Soviet control and the resilience of anti-communist movements.
From Brinkmanship to Détente
The 1970s saw a shift from intense Cold War brinkmanship to détente, a period of relaxed tensions and improved relations between the superpowers. Key treaties such as the SALT I (Strategic Arms Limitation Talks) agreement and the Helsinki Accords were milestones in this era.
Détente Cools
Détente began to wane in the late 1970s and early 1980s due to renewed tensions. The Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, combined with the election of Ronald Reagan as U.S. President, led to a resurgence of Cold War hostilities and a renewed arms race.
Situation in Russia
The late 1980s were marked by significant changes in the Soviet Union under Mikhail Gorbachev. Gorbachev’s policies of glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) aimed at reforming the Soviet system but also contributed to increased calls for independence among Soviet republics.
Case of Germany
Germany’s division and subsequent reunification were central to Cold War dynamics. The Berlin Wall, erected in 1961, symbolized the divide between East and West. The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 became a powerful symbol of the end of the Cold War, leading to the reunification of Germany in 1990.
Unrest in the Soviet Union
By the late 1980s, the Soviet Union faced widespread unrest and economic difficulties. Nationalist movements gained momentum, and public dissatisfaction with the communist regime grew. This unrest contributed to the eventual dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Downfall of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union officially dissolved on December 26, 1991, marking the end of the Cold War. The republics of the Soviet Union became independent states, and the Cold War’s bipolar world order gave way to a new era of international relations.
Impact of the Cold War
The Cold War profoundly shaped global politics and economics, leading to:
- The Bipolar World Order: The division of the world into two opposing blocs.
- Nuclear Arms Race: Development and stockpiling of nuclear weapons.
- Proxy Wars: Numerous conflicts in third-world countries influenced by superpower rivalries.
- Ideological Influence: The spread of capitalism and communism as competing ideologies.
- Geopolitical Realignments: Changes in alliances and global power structures.
The Cold War’s legacy continues to influence international relations and global politics today. The end of the Cold War ushered in a unipolar world dominated by the U.S., with significant implications for global diplomacy, economics, and security.
TIME LINE OF COLD WAR
| Year | Event |
|---|
| 1945 | Yalta Conference: Meeting between Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin to plan post-war Europe. |
| 1947 | Truman Doctrine: U.S. policy to support countries resisting communism. |
| 1947 | Marshall Plan: U.S. economic aid to rebuild European economies and prevent communism. |
| 1948-49 | Berlin Blockade: Soviet blockade of West Berlin, leading to a Western airlift. |
| 1949 | NATO Formation: Creation of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization as a collective security alliance. |
| 1949 | Soviet Union Tests First Atomic Bomb: Marking the beginning of the nuclear arms race. |
| 1950-1953 | Korean War: Conflict between North Korea (supported by China and USSR) and South Korea (supported by U.S. and UN). |
| 1954-1975 | Vietnam War: Conflict in Vietnam involving North Vietnamese (supported by USSR and China) and South Vietnamese (supported by U.S. and allies). |
| 1955 | Warsaw Pact Formation: Soviet-led military alliance in response to NATO. |
| 1956 | Hungarian Uprising: A failed revolt against Soviet control in Hungary. |
| 1957 | Sputnik Launch: The USSR launches the first artificial satellite, initiating the space race. |
| 1961 | Berlin Wall Erected: Physical division between East and West Berlin symbolizing Cold War divisions. |
| 1962 | Cuban Missile Crisis: A 13-day confrontation over Soviet missiles in Cuba, bringing the U.S. and USSR to the brink of nuclear war. |
| 1964 | Gulf of Tonkin Incident: U.S. Congress passes the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, escalating U.S. involvement in Vietnam. |
| 1968 | Prague Spring: A period of political liberalization in Czechoslovakia crushed by Soviet intervention. |
| 1972 | SALT I Agreement: First Strategic Arms Limitation Talks agreement between the U.S. and the USSR. |
| 1973 | Paris Peace Accords: Agreement intended to end the Vietnam War and restore peace in Vietnam. |
| 1979 | Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan: Soviet military intervention, leading to U.S. support for Afghan resistance. |
| 1983 | Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI): U.S. proposal for a missile defense system, also known as “Star Wars.” |
| 1985 | Gorbachev Becomes Soviet Leader: Introduction of reforms like Glasnost and Perestroika. |
| 1989 | Fall of the Berlin Wall: Marking the beginning of the end of the Cold War and the eventual reunification of Germany. |
| 1991 | Dissolution of the Soviet Union: Official end of the USSR, leading to the end of the Cold War. |
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Discuss the primary causes that led to the Cold War. How did ideological differences and geopolitical strategies contribute to the prolonged tension between the United States and the Soviet Union?
Analyze the impact of the Soviet Union’s control over Eastern Europe on the geopolitical dynamics of the Cold War. How did Soviet policies influence the political landscape of the region?
Evaluate the effectiveness of the United States’ containment strategy during the Cold War. Consider key policies such as the Truman Doctrine, Marshall Plan, and NATO in your analysis.
Examine the significance of the Cuban Missile Crisis in the context of the Cold War. How did this confrontation impact U.S.-Soviet relations and global security?
Discuss the role of the Vietnam War as a Cold War conflict. How did the involvement of superpowers affect the course and outcome of the war?
Assess the impact of the Cold War on the Middle East, particularly focusing on conflicts such as the Six-Day War and the Yom Kippur War. How did superpower interests shape the region’s geopolitical landscape?
Critically analyze the reasons for the deterioration of détente and the resurgence of Cold War tensions in the late 1970s and early 1980s. How did the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan contribute to this shift?
Explain the factors leading to the collapse of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War. How did internal challenges within the Soviet Union and external pressures contribute to its dissolution?
1. COLONIALISM
Colonialism denotes a specific phase in the historical evolution of a colony, situated between traditional and modern capitalist economies. During this phase, the economy and society are predominantly controlled by a foreign capitalist class. The colonial economy is characterized as neither pre-capitalist nor capitalist but as a hybrid system.
DEFINITION
Colonialism is a socio-economic formation where multiple modes of production coexist, including feudalism, petty commodity production, agrarian systems, and industrial and finance capitalism. Surplus value is extracted through control over state power.
BASIC FEATURES OF COLONIALISM
- The colony is integrated into the global capitalist system in a subordinate role.
- There is an unequal exchange between the source (colony) and the destination (metropolis), leading to a drain of wealth.
- The source produces goods of low value and productivity with limited technology (raw materials), while the destination produces high-value goods with advanced technology (manufactured goods).
- Foreign political domination characterizes colonialism, as highlighted by Indian nationalist leader Bal Gangadhar Tilak’s metaphor of “decorating another’s wife.”
Colonialism led to the domination of all indigenous classes within the colony. The colonial state ensured law and order and safeguarded its own security from internal and external threats. It undertook significant transformations of the social, economic, cultural, political, and legal frameworks of the colony to facilitate its extensive reproduction.
STAGES OF COLONIALISM
India experienced the first and second stages of colonialism, Egypt went through the third stage, and Indonesia experienced the first and third stages.
First Stage: Monopoly Trade and Plunder Colonialism
- In this stage, colonial powers engaged in acquiring cheaper inputs, imposing high duties on exports, excluding local traders, and competing with other European powers for trade monopoly. This period was marked by the plundering of wealth through these exploitative practices.
Second Stage: Era of Free Trade
- This stage involved significant economic, political, and administrative changes aimed at facilitating exploitation through a new mode of trade. The focus was on development and modernization, allowing capitalists to establish plantations, trade, transport, mining, and industries. Improvements were made in transport and communication systems, and liberal imperialism emerged as the new political ideology.
Third Stage: Era of Finance Capital
- Large-scale capital accumulation in metropolitan countries led to a search for investment opportunities abroad. The ideology of benevolent despotism emerged, with the colonial subjects seen as perpetual dependents in need of guardians. This stage often failed to take off due to the severe economic damage inflicted on some colonies, making them incapable of absorbing substantial capital investments.
COLONIALISM IN DIFFERENT TERRITORIES
AFRICA
British territories included Nigeria, Gold Coast, Gambia, Sierra Leone, Kenya, Tanganyika, Nyasaland, Uganda, North and South Rhodesia, and South Africa. French colonies included Algeria, Morocco, Cameroon, French-Congo, Tunisia, and Madagascar.
Impact
The impact of colonialism in Africa was profound:
- Self-sufficient African economies were disrupted, subordinated, and transformed under colonial rule, leading to significant debt burdens (e.g., the Suez Canal).
- Class differentiation emerged.
- The interconnections between African countries and with other parts of the world were severely disrupted.
CASE OF EGYPT
Under British rule, Egypt was developed primarily as a supplier of cotton for the British textile industry. This single-crop dependency proved disastrous, as Egypt became reliant on imports for essential food supplies. Control over the cotton industry, from land ownership and processing to transportation, was dominated by foreigners, leading to severe indebtedness due to exploitation.
CONCLUSION
Colonialism is a modern historical phenomenon closely linked with industrial capitalism. While metropolitan centers experienced growth under capitalism, colonies faced underdevelopment. Colonialism represents the exploitation and transformation of colonies, while imperialism pertains to the economic and political dominance exerted by the metropolitan centers.
2. IMPERIALISM
DEFINITION
Imperialism is a system where a dominant country exerts political control over the domestic and foreign policies and internal politics of another country, referred to as the periphery. Unlike pre-modern forms of conquest, imperialism is a distinctly modern phenomenon characterized by:
- A sharp increase in the international flow of commodities, people, and capital.
- An interdependent network of relationships between countries at various levels of industrial development.
- Advanced and superior technology in imperialist countries.
- Competition among advanced capitalist countries.
EMPIRE VERSUS IMPERIALISM
In the capitalist era, empire equates to imperialism. Unlike earlier forms where the primary goal was to extract tribute, capitalist imperialism transformed and manipulated the economies and societies of conquered areas to serve the interests of capital accumulation in the imperialist countries at the core of the economic hierarchy.
COLONIALISM
| Colonialism | |
|---|---|
| Definition | Colonialism involves the direct establishment and governance of colonies in foreign territories. |
| Control | Colonial powers exercise direct control through appointed officials and military presence. |
| Motive | The primary motives are acquiring resources, cheap labor, and expanding territorial control. |
| Governance | Colonies are governed by officials sent from the colonial power, imposing their own laws and institutions. |
| Scope | Colonialism typically focuses on establishing settlements and directly controlling specific territories. |
| Examples | British colonization of India, French colonization of Algeria. |
MODES OF IMPERIALISM
Formal imperialism involves direct annexation and rule, while informal empire denotes indirect rule where local elites are legally independent but politically dependent on the dominant power.
The new imperialism extended into the periphery (Asia and Africa) reflecting the political struggles within Europe. For the British, it meant securing routes to India through Egypt and the Suez Canal, which required control over the Nile’s headwaters and a prominent position in North Africa. For the French and Germans, it signified acquiring “places in the sun” to demonstrate national prestige.
Mercantilism and Early Trading Empires
The competitive environment among European powers led to advancements in military techniques and economic progress. The dramatic growth of trans-Atlantic trade catalyzed the establishment of empires, with developments in shipbuilding and navigation technology enabling European dominance. Charter companies facilitated empire management with minimal cost to states, which later transitioned to direct royal control.
Britain, as a leader, benefited from a developed banking and financial system, geographic advantage, and being the first to undergo the Industrial Revolution. This conferred significant advantages in dominating Europe and acquiring colonies.
INDUSTRIAL CAPITALISM—IMPERIALISM OF FREE TRADE
The Industrial Revolution in Britain marked a pivotal moment when Britain was the preeminent global power, dominating as the sole imperialist, importer, exporter, and foreign investor. The early British industrial economy relied heavily on foreign trade for expansion. Overseas markets for products and capital outlets were essential. By 1815, Britain’s dominance, supported by naval superiority, financial credit, and commercial enterprise, was firmly established.
As industrial capitalism spread, the need for colonies grew as markets for manufactured goods and sources of raw materials. Colonies became subordinate trading partners, with their economic surplus appropriated through trade characterized by unequal exchange.
From the mid-twentieth century, decolonization and the rise of multinational corporations, international donor agencies, and global economic mechanisms led to what is known as Neo-colonialism. This period marked a shift from direct colonial control to a more nuanced form of economic and political influence.
The world history from the late fifteenth to the mid-twentieth century was characterized by European domination, with Britain initially as the uncontested global power. Since 1870, this dominance faced challenges from other industrializing European nations. Even after formal colonial rule ended, the influence of Britain and later the US persisted through multinational banks, financial institutions, and democratic frameworks.
PRACTICE QUESTIONS
Discuss the economic motivations behind European colonial expansion in the 19th century.
Analyze how industrialization and the search for new markets influenced European powers to pursue imperialistic policies.Evaluate the impact of colonial rule on the social and cultural structures of one African country during the 19th and early 20th centuries.
Provide specific examples of changes in social hierarchy, culture, and traditional practices.Analyze the role of the Berlin Conference (1884-1885) in shaping the modern political boundaries of Africa.
How did the conference’s decisions affect the colonial and post-colonial landscape of the continent?Compare and contrast the colonial policies of the British and French empires in Asia.
How did the administrative and economic strategies of these two powers differ, and what were the impacts on their respective colonies?Assess the effects of imperialism on the economic development of Latin America in the 19th and early 20th centuries.
Examine how imperialist policies influenced trade, investment, and industrialization in Latin American countries.Discuss the concept of “civilizing mission” as used by European colonial powers.
How did this ideology justify imperialism, and what were its real-world implications for the colonies?Examine the impact of World War I on the dynamics of colonial empires.
How did the war alter the relationships between colonial powers and their colonies, and what were the immediate post-war consequences for the colonial world?Evaluate the role of nationalist movements in the decolonization process of one Asian or African country in the mid-20th century.
How did nationalist leaders and movements contribute to the end of colonial rule and the emergence of independent states?
